Biology:Sesbania sesban
| Sesbania sesban | |
|---|---|
| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Rosids |
| Order: | Fabales |
| Family: | Fabaceae |
| Subfamily: | Faboideae |
| Genus: | Sesbania |
| Species: | S. sesban
|
| Binomial name | |
| Sesbania sesban (L.) Merr.
| |
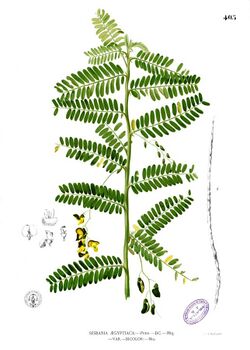
Sesbania sesban, the Egyptian riverhemp,[1] is a species of plant in the legume family, a fast growing species, it has four varieties that are currently recognized.[2][3]
Synonyms include:
- Aeschynomene aegyptiaca (Pers.) Steud.
- Aeschynomene sesban L.
- Emerus sesban (L.) Kuntze
- Sesbania aegyptiaca Poir.
Description
A perennial shrub or small tree that grows up to 6 m tall sometimes reaching 8 m.[citation needed] It has paripinnately compound leaves with between 6-27 pairs of linear to oblong leaflets per pinnae; the leaves and rachis tend to be pilose. Flowers are yellow in color with brown and purple streaks on the corolla.
Distribution and habitat
Sesbania seban occurs widely in tropical East and West Africa, in Southern Africa and in Asia.[4] Commonly found on a variety of soil types including loose sandy soil and clay soil, it grows in areas with annual rainfall of between 500-2000 mm.[3]
Infraspecies
- Sesbania sesban var. bicolor (Wight & Arn.) F.W.Andrews
- Sesbania sesban var. nubica Chiov.
- Sesbania sesban subsp. punctata (DC.) J.B.Gillett
- Sesbania sesban subsp. sesban
Uses
Sesbania sesban is a nitrogen-fixing tree and may be useful in alley cropping. It is also used as a fodder crop and source of fuel wood.[5]
References
- ↑ "Sesbania sesban". Natural Resources Conservation Service PLANTS Database. USDA. https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=SESE8. Retrieved 10 November 2015.
- ↑ "Sesbania sesban (L.) Merr. | Plants of the World Online | Kew Science" (in en). http://powo.science.kew.org/taxon/urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:518533-1.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Heering, J.H. (1995). Botanical and agronomic evaluation of a collection of Sesbania sesban and related perennial species (PhD thesis). Wageningen University.
- ↑ Heering, J. H.; Nokoe, S.; Jemal, M. (1996). "The classification of a Sesbania sesban (sesban) collection. I. Morphological attributes and their taxonomic significance" (in en). Tropical Grasslands 30 (2). ISSN 0049-4763. https://cgspace.cgiar.org/handle/10568/27807.
- ↑ Palsaniya, Dana Ram; Kumar, T. Kiran; Chaudhary, Manoj; Choudhary, Mukesh; Prasad, Mahendra; Kumar, Sunil (2023-10-15). "Tillage practices and mulching affect system productivity, profitability and energy use in Sesbania alley based food - fodder systems under rainfed agro-ecosystems of semi-arid tropics". Field Crops Research 302: 109104. doi:10.1016/j.fcr.2023.109104. ISSN 0378-4290. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0378429023002976.
Relevant literature
- Ramni Jamnadass, Jean Hanson, Jane Poole, Olivier Hanotte, Tony J. Simons, Ian K. Dawson. High differentiation among populations of the woody legume Sesbania sesban in sub-Saharan Africa: Implications for conservation and cultivation during germplasm introduction into agroforestry systems. Forest Ecology and Management Volume 210, Issues 1–3, 2005, Pages 225–238, ISSN 0378-1127, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2005.02.033.
External links
Wikidata ☰ Q3206585 entry
 |

