Biology:Spotted antbird
| Spotted antbird | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Passeriformes |
| Family: | Thamnophilidae |
| Genus: | Hylophylax |
| Species: | H. naevioides
|
| Binomial name | |
| Hylophylax naevioides (Lafresnaye, 1847)
| |
| |
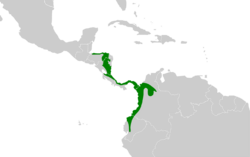
The spotted antbird (Hylophylax naevioides) is a species of bird in the family Thamnophilidae. In southern Central America, it is found in Honduras, Nicaragua, Costa Rica and Panama; also Colombia and Ecuador of northwestern South America. Its natural habitat is subtropical or tropical moist lowland forests.
Description

File:Spotted Antbird.tif A smallish bird, measuring 11 cm (4.3 in) and weighing 16–19.5 g (0.56–0.69 oz). The male spotted antbird's plumage is a distinctive combination of a necklace of large black spots on a white chest, chestnut back, grey head, and black throat. The female is a duller version of the male, but also distinctive with large chest spots and two wide buffy wing-bars.[2]
Distribution and habitat
Forages as individuals or pairs in lower levels of mature, humid forests. Found in lowlands and foothills up to 1,000 m (3,300 ft).[2][3]
Behaviour
Spotted antbirds are known to follow army ant swarms to catch insects and other small animals trying to flee. They eat spiders, scorpions, cockroaches, katydids, crickets, centipedes, sowbugs, moths, beetles, caterpillars, ants, bristletails and, on occasion, lizards and frogs.
This bird is an open-cup nesting species that lays an average clutch of 2 maroon-splotched white eggs,[4][5] which both adults incubate.[6] The nestling period is 11 days.[4][6]
References
- ↑ BirdLife International (2016). "Hylophylax naevioides". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2016: e.T22701911A93854354. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22701911A93854354.en. https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/22701911/93854354. Retrieved 12 November 2021.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Angehr, George R.; Dean, Robert (2010). The Birds of Panama: A Field Guide. Zona Tropical. pp. 214–215. ISBN 978-0-8014-7674-7.
- ↑ Garrigues, Richard; Dean, Robert (2007). The Birds of Costa Rica: A Field Guide. Zona Tropical. pp. 180–181. ISBN 978-0-8014-7373-9.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Skutch, Alexander F. (1945). "Incubation and nestling periods of Central American birds". The Auk 62 (1): 8–37. doi:10.2307/4079958. https://sora.unm.edu/sites/default/files/journals/auk/v062n01/p0008-p0037.pdf.
- ↑ "Life History - Spotted Antbird". The Cornell Lab of Ornithology, Cornell University. http://neotropical.birds.cornell.edu/portal/species/lifehistory?p_p_spp=398771.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Skutch, Alexander F. (1969). "Spotted antbird". Life Histories of Central American Birds III: Families Cotingidae, Pipridae, Formicariidae, Furnariidae, Dendrocolaptidae, and Picidae. Pacific Coast Avifauna, Number 35. Berkeley, California: Cooper Ornithological Society. pp. 245–247. https://sora.unm.edu/sites/default/files/journals/pca/pca_035.pdf#page=245.
Further reading
Styrsky, J.N.; Brawn, J.D. (2011). "Annual fecundity of a Neotropical bird during years of high and low rainfall". Condor 11 (1): 194–199. doi:10.1525/cond.2011.100051.
- Willis, Edwin O. (1972). The Behavior of Spotted Antbirds. Onithological Monographs 10. Lawrence, Kansas: American Ornithologists' Union. https://sora.unm.edu/sites/default/files/journals/om/om010.pdf.
External links
- "Spotted antbird media". Internet Bird Collection. http://www.hbw.com/ibc/species/spotted-antbird-hylophylax-naevioides.
- Spotted antbird photo gallery at VIREO (Drexel University)
Wikidata ☰ Q1274102 entry
 |

