Biology:Synodontis nummifer
| Synodontis nummifer | |
|---|---|
| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Actinopterygii |
| Order: | Siluriformes |
| Family: | Mochokidae |
| Genus: | Synodontis |
| Species: | S. nummifer
|
| Binomial name | |
| Synodontis nummifer Boulenger, 1899
| |
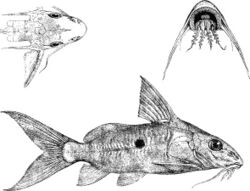
Synodontis nummifer, known as the two spot synodontis,[2][3] is a species of upside-down catfish native to the Congo Basin of Cameroon, the Democratic Republic of the Congo and the Republic of the Congo.[4] It was first described by the Belgian-British zoologist George Albert Boulenger in 1899, based upon a holotype discovered in Léopoldville, Belgian Congo.[3] The specific name "nummifer" comes from the Latin for "to bear a coin", which refers to the large spots on its sides.[2]
Description
The body of the fish is olive colored on the back transitioning to whitish on the underside.[5] The sides of the fish have a large round black spot on each side, above the lateral line, and frequently a second spot above the base of the anal fin.[5] The pigmentation of the head is spotted.[3]
Like other members of the genus, this fish has a humeral process, which is a bony spike that is attached to a hardened head cap on the fish and can be seen extending beyond the gill opening.[2] This process is broad and rounded at the end, and extends as far as the occipito-nuchal process.[5] The first ray of the dorsal fin and the pectoral fins have a hardened first ray which is serrated,[2] as long or a little longer than the head.[5] The caudal fin is very deeply forked.[5] It has short, cone-shaped teeth in the upper jaw.[2] In the lower jaw, the teeth are s-shaped and movable.[2] The fish has one pair of maxillary barbels, with broad membranes at the base, as long as the head or slightly shorter,[5] and two pairs of mandibular barbels that are often branched.[2][3] The adipose fin is about four times as long as it is deep.[5] The pectoral spine is a little shorter than the head, and strongly serrated on both sides.[5]
This species grows to a length of 17.5 centimetres (6.9 in) SL although specimens up to 20.5 centimetres (8.1 in) TL have been recorded in the wild.[2][4]
Habitat
In the wild, the species inhabits tropical waters with a temperature range of 22 to 25 °C (72 to 77 °F), a pH of 6.4 – 7.2, and dH range of up to 18.[4] It has been found throughout the Congo River basin, but not the southern tributaries of the Congo River.[6]
Parasites
As other fish, Synodontis nummifer harbours parasites, including species of the monogenean genus Synodontella.[7]
References
- ↑ Moelants, T. (2010). "Synodontis nummifer". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2010: e.T182684A7942307. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2010-3.RLTS.T182684A7942307.en. https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/182684/7942307. Retrieved 20 November 2021.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 2.7 "Synodontis nummifer Boulenger, 1899". Planet Catfish. 17 Jan 2009. http://www.planetcatfish.com/common/species.php?species_id=550. Retrieved 17 October 2016.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 "Synodontis nummifer Boulenger, 1899". scotcat.com. http://www.scotcat.com/mochokidae/s_nummifer.htm. Retrieved 17 October 2016.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Froese, Rainer and Pauly, Daniel, eds. (2016). "Synodontis nummifer" in FishBase. June 2016 version.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 5.6 5.7 Boulenger, George Albert (1909). Catalogue of the fresh-water fishes of Africa in the British museum (Natural history). London: British Museum. pp. 463–465. https://archive.org/stream/cu31924024781837/#page/n481/mode/1up.
- ↑ Moelants, T. (2010). "Synodontis nummifer". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2010: e.T182684A7942307. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2010-3.RLTS.T182684A7942307.en. https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/182684/7942307. Retrieved 15 January 2018.
- ↑ Mbondo, Jonathan A.; Nack, Jacques; Bitja Nyom, Arnold R.; Pariselle, Antoine; Bilong Bilong, Charles F. (2019). "New species of Synodontella (Monogenea, Ancyrocephalidae) gill parasites of two Synodontis spp. (Pisces, Mochokidae) from the Boumba River (Congo Basin, East Cameroon)". Parasite 26: 37. doi:10.1051/parasite/2019037. ISSN 1776-1042. PMID 31246168.
External links
Wikidata ☰ Q3757795 entry
 |


