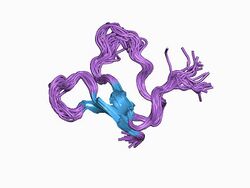
Tachystatins are antimicrobial chitin-binding peptides from Japanese horseshoe crab. Amino acid residues Tyr(14) and Arg(17) in Tachystatin B are thought to be the essential residues for chitin binding.[2] These small proteins contain a cysteine-stabilised triple-stranded beta-sheet with an inhibitor cystine knot motif and show features common to membrane-interactive peptides. Tachystatin A is thought to have an antimicrobial activity similar to defensins.[1]
References
 | Original source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tachystatin. Read more |