Biology:Tharosaurus
| Tharosaurus | |
|---|---|
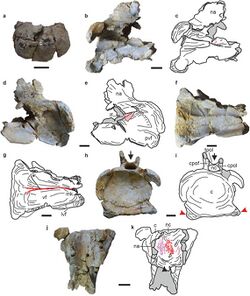
| |
| Cervical vertebrae of the holotype | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Script error: No such module "Taxobox ranks".: | Animalia |
| Script error: No such module "Taxobox ranks".: | Chordata |
| Script error: No such module "Taxobox ranks".: | Dinosauria |
| Script error: No such module "Taxobox ranks".: | Saurischia |
| Script error: No such module "Taxobox ranks".: | †Sauropodomorpha |
| Script error: No such module "Taxobox ranks".: | †Sauropoda |
| Script error: No such module "Taxobox ranks".: | †Diplodocoidea |
| Script error: No such module "Taxobox ranks".: | †Dicraeosauridae |
| Script error: No such module "Taxobox ranks".: | †Tharosaurus Bajpai et al., 2023 |
| Script error: No such module "Taxobox ranks".: | <div style="display:inline" class="script error: no such module "taxobox ranks".">†T. indicus |
| Binomial name | |
| †Tharosaurus indicus Bajpai et al., 2023
| |
Tharosaurus (meaning "Thar desert lizard") is an extinct genus of dicraeosaurid sauropod dinosaur from the Middle Jurassic Jaisalmer Formation of India. The genus contains a single species, T. indicus, known from several vertebrae and a rib. Tharosaurus represents the earliest diplodocoid currently known and the first described from India.[1]
Discovery and naming

The Tharosaurus holotype specimen, RWR-241 (A–K), was discovered between 2019 and 2021 in sediments of the Jaisalmer Formation near Jethwai village in Jaisalmer district of Rajasthan state in western India.[2] The specimen consists of partial cervical, dorsal, and caudal vertebrae and a dorsal rib.[1]
In 2023, Bajpai et al. described Tharosaurus indicus as a new genus and species of dicraeosaurid sauropod based on these fossil remains. The generic name, "Tharosaurus", combines a reference to the Thar desert where the holotype was found with the Greek word "sauros", meaning "lizard". The specific name, "indicus", refers to the discovery of the specimen in India.[1]
Classification
Bajpai et al. (2023) recovered Tharosaurus as an early-diverging dicraeosaurid, suggesting it represents a relic of a lineage that evolved in India and later spread across the world. Tharosaurus is the oldest dicraeosaurid, as well as the oldest diplodocoid. The results of their phylogenetic analyses are shown in the cladogram below:[1]
| Diplodocoidea |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Paleoenvironment
The Jaisalmer Formation represents a deposit on the Tethyan coast of India. Other dinosaurs from this environment include a large theropod and a turiasaur, both known only from teeth.[3][4] Several ichnofossils are also known from the formation.[5]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Bajpai, S.; Datta, D.; Pandey, P.; Ghosh, T.; Kumar, K.; Bhattacharya, D. (2023). "Fossils of the oldest diplodocoid dinosaur suggest India was a major centre for neosauropod radiation". Scientific Reports 13 (1): 12680. doi:10.1038/s41598-023-39759-2. PMID 37542094. Bibcode: 2023NatSR..1312680B.
- ↑ Ghosh, Sahana (13 September 2023). "Fossil find is earliest record of a plant-eating dinosaur group". https://www.nature.com/articles/d44151-023-00135-8.
- ↑ Sharma, A.; Hendrickx, C.; Singh, S. (2023). "First theropod record from the Marine Bathonian of Jaisalmer Basin, Tethyan Coast of Gondwanan India". Rivista Italiana di Paleontologia e Stratigrafia 129 (1): 49–64. doi:10.54103/2039-4942/18306.
- ↑ "The first turiasaurian sauropod of India reported from the Middle Jurassic (Bathonian) sediments of Jaisalmer Basin, Rajasthan, India". Neues Jahrbuch für Geologie und Paläontologie - Abhandlungen 304 (2): 187–203. 2022. doi:10.1127/njgpa/2022/1064.
- ↑ Kulkarni, Kantimati; Borkar, Vidyadhar D.; Dashputre, Tejashree (2008). "Ichnofossils from the Fort Member (Middle Jurassic), Jaisalmer Formation, Rajasthan". Journal of the Geological Society of India 71 (5): 731–738. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/261263004.
Wikidata ☰ Q121179093 entry
 |
