Biology:Transverse plane
From HandWiki
Short description: Anatomical plane that divides the body into superior and inferior parts
| Transverse plane | |
|---|---|
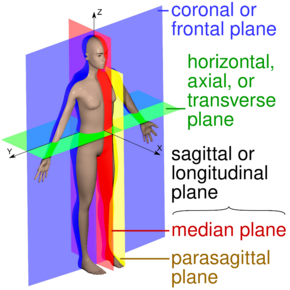 The main anatomical planes of the human body, including median (red), paramedian (yellow), frontal or coronal plane (blue) and transverse or axial plane (green) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | plana transversalia |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The transverse plane (also known as the horizontal plane, axial plane and transaxial plane) is an anatomical plane that divides the body into superior and inferior sections. It is perpendicular to the coronal and sagittal planes.
List of clinically relevant anatomical planes
- Transverse thoracic plane
- Xiphosternal plane (or xiphosternal junction)
- Transpyloric plane
- Subcostal plane
- Umbilical plane (or transumbilical plane)
- Supracristal plane
- Intertubercular plane (or transtubercular plane)
- Interspinous plane
Clinically relevant anatomical planes with associated structures
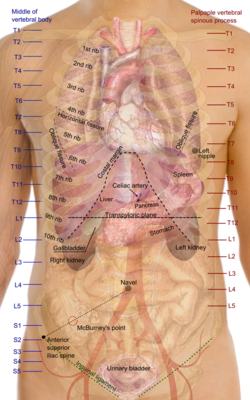
- The transverse thoracic plane
- Plane through T4 & T5 vertebral junction and sternal angle of Louis.
- Marks the:
- Attachment of costal cartilage of rib 2 at the sternal angle;
- Aortic arch (beginning and end);
- Upper margin of SVC;
- Thoracic duct crossing;
- Tracheal bifurcation;
- Pulmonary trunk bifurcation;
- The xiphosternal plane (a.k.a. xiphosternal junction)
- The transpyloric plane
- Plane located halfway between the jugular notch and the upper border of the symphysis pubis;
- Typically located at the lower border of L1;
- Cuts through the pylorus and the tips of the ninth costal cartilages;
- The subcostal plane
- Transverse plane through the inferior border of costal margin;
- Typically located at the superior border of L3, or transects L3;
- The umbilical plane (or transumbilical plane)
- Located at the level of L3/L4 vertebral junction or IV disc;
- The supracristal plane
- Located at the level of L4;
- Marks bifurcation of aorta;
- Most superior aspect of iliac crest;
- The intertubercular plane (a.k.a. Transtubercular plane)
- Located at the level of L5;
- Marks origin of IVC;
- The interspinous plane
- Transverse plane which transverses the anterior superior iliac spines.
- Typically located at the level of S1.
See also
- Anatomical terms of location
- Horizontal plane
- Coronal plane
- Sagittal plane
References
 |
