Biology:Vachellia
| Vachellia | |
|---|---|

| |
| Vachellia farnesiana | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Rosids |
| Order: | Fabales |
| Family: | Fabaceae |
| Subfamily: | Caesalpinioideae |
| Clade: | Mimosoid clade |
| Genus: | Vachellia Wight & Arn. |
| Type species | |
| Vachellia farnesiana (L.) Wight & Arn.
| |
| Species | |
|
147; see text. | |
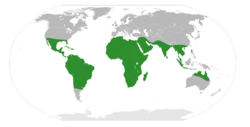
| |
| The original range of the genus Vachellia. Today it is also found in most Mediterranean countries. | |
| Synonyms[1] | |
| |
Vachellia is a genus of flowering plants in the legume family, Fabaceae, commonly known as thorn trees or acacias. It belongs to the subfamily Mimosoideae. Its species were considered members of genus Acacia until 2009.[2][3] Vachellia can be distinguished from other acacias by its capitate inflorescences and spinescent stipules.[4] Before discovery of the New World, Europeans in the Mediterranean region were familiar with several species of Vachellia, which they knew as sources of medicine, and had names for them that they inherited from the Greeks and Romans[clarification needed].[5]
The wide-ranging genus occurs in a variety of open, tropical to subtropical habitats, and is locally dominant.[6] In parts of Africa, Vachellia species are shaped progressively by grazing animals of increasing size and height, such as gazelle, gerenuk, and giraffe. The genus in Africa has thus developed thorns in defence against such herbivory [clarification needed].[7]
Nomenclature
By 2005, taxonomists had decided that Acacia sensu lato should be split into at least five separate genera. The ICN dictated that under these circumstances, the name of Acacia should remain with the original type, which was Acacia nilotica.[1] However, that year the General Committee of the IBC decided that Acacia should be given a new type (Acacia verticillatum) so that the ~920 species of Australian acacias would not need to be renamed Racosperma. This decision was opposed by 54.9% or 247 representatives at its 2005 congress, while 45.1% or 203 votes were cast in favor. However, since a 60% vote was required to override the committee, the decision was carried, and a nom. cons. propositum was listed in Appendix III (p. 286).[8][9] The 2011 congress voted 373 to 172 to uphold the 2005 decision, which means that the name Acacia and a new type follow the majority of the species in Acacia sensu lato, rather than this genus.[10] However, some members of the botanical community remain unconvinced,[11] and the use of Acacia in the scientific literature continues to exceed the use of the new generic names.
Description
The members of Vachellia are trees or shrubs, sometimes climbing, and are always armed. Younger plants, especially, are armed with spines which are modified stipules, situated near the leaf bases. Some (cf. V. tortilis, Vachellia hebeclada ({{{2}}}), V. luederitzii and V. reficiens) are also armed with paired, recurved prickles (in addition to the spines).[12] The leaves are alternate and bipinnately arranged, and their pinnae are usually opposite. The racemose inflorescences usually grow from the leaf axils. The yellow or creamy white flowers are produced in spherical heads, or seldom in elongate spikes, which is the general rule in the related genus Senegalia. The flowers are typically bisexual with numerous stamens, but unisexual flowers have been noted in V. nilotica (cf. Sinha, 1971).[13] The calyx and corolla are usually 4 to 5-lobed. Glands are usually present on the rachis and the upper side of the petiole. The seed pod may be straight, curved or curled, and either dehiscent or indehiscent.[12]
-
V. vernicosa, or "viscid acacia", in habitat, Far West Texas
-
V. vernicosa, detail of inflorescence
Species list
Of the 163 species currently assigned to Vachellia, 52 are native to the Americas, 83 to Africa, Madagascar and the Mascarene Islands, 32 to Asia and 9 to Australia and the Pacific Islands.[14] Vachellia comprises the following species:[15][2][16][17][3][18][19][20][21]
- Vachellia abyssinica (Hochst. ex. Benth.) Kyal. & Boatwr.—flat top acacia
- subsp. abyssinica (Hochst. ex. Benth.) Kyal. & Boatwr.
- subsp. calophylla (Brenan) Kyal. & Boatwr.
- Vachellia acuifera (Benth.) Seigler & Ebinger—Bahama acacia, cassip, pork-and-doughboy, (Bahamas) rosewood
- Vachellia albicortata (Burkart) Seigler & Ebinger
- Vachellia allenii (D. H. Janzen) Seigler & Ebinger—Allen acacia
- Vachellia amythethophylla (Steud. ex A.Rich.) Kyal. & Boatwr.
- Vachellia ancistroclada (Brenan) Kyal. & Boatwr.
- Vachellia anegadensis (Britton) Seigler & Ebinger—Anegada acacia, blackbrush-wattle, pokemeboy
- Vachellia antunesii (Harms) Kyal. & Boatwr.
- Vachellia arenaria (Schinz) Kyal. & Boatwr.—sand acacia
- Vachellia aroma (Gillies ex Hook. & Arn.) Seigler & Ebinger
- var. aroma Gillies ex Hook. & Arn.
- var. huarango Ruíz & J.Macbr.
- Vachellia astringens (Gillies in Hook. et Arn.) Speg.
- Vachellia baessleri Clarke, Siegler & Ebinger
- Vachellia barahonensis (Urb. & Ekman) Seigler & Ebinger
- Vachellia bavazzanoi (Pichi-Sermolli) Kyal. & Boatwr.
- Vachellia belairioides (Urb.) Seigler & Ebinger—Bellair acacia
- Vachellia bellula (Drake) Boatwr.
- Vachellia biaciculata (S. Watson) Seigler & Ebinger
- Vachellia bidwillii (Benth.) Kodela—corkwood wattle, dogwood. "'Waneu', of the aboriginals of Central Queensland ; 'Yadthor', of those of the Cloncurry River, Northern Queensland."[22]
- Vachellia bilimekii (J. Macbr.) Seigler & Ebinger
- Vachellia bolei (R.P. Subhedar) Ragupathy, Seigler, Ebinger & Maslin[23]
- Vachellia borleae (Burtt Davy) Kyal. & Boatwr.—sticky acacia, named for the collector Jeanne M. Borle.
- Vachellia brandegeana (I. M. Johnst.) Seigler & Ebinger—Baja California acacia
- Vachellia bravoensis (Isely) Seigler & Ebinger
- Vachellia bricchettiana (Chiov.) Kyal. & Boatwr.
- Vachellia bucheri (Marie-Victorín) Seigler & Ebinger—Bucher acacia
- Vachellia bullockii (Brenan) Kyal. & Boatwr.
- var. bullockii (Brenan) Kyal. & Boatwr.
- var. induta (Brenan) Kyal. & Boatwr.
- Vachellia burttii (Bak. f.) Kyal. & Boatwr.
- Vachellia bussei (Harms ex Sjöstedt) Kyal. & Boatwr.
- Vachellia californica (Brandegee) Seigler & Ebinger
- Vachellia campechiana (Mill.) Seigler & Ebinger—boatthorn acacia, spoon-thorn acacia
- f. campechiana (Mill.) Seigler & Ebinger
- f. houghii (Britton & Rose) Seigler & Ebinger
- Vachellia caurina (Barneby & Zanoni) Seigler & Ebinger
- Vachellia caven (Molina) Seigler & Ebinger
- var. caven (Molina) Seigler & Ebinger
- var. dehiscens (Ciald.) Seigler & Ebinger
- var. microcarpa (Speg.) Seigler & Ebinger
- var. stenocarpa (Speg.) Seigler & Ebinger
- Vachellia cernua (Thulin & Hassan) Kyal. & Boatwr.
- Vachellia chiapensis (Saff.) Seigler & Ebinger—Chiapas acacia
- Vachellia choriophylla (Benth.) Seigler & Ebinger—cinnecord acacia, Florida acacia, (Bahamas) cinnecord
- Vachellia clarksoniana (Pedley) Kodela
- Vachellia collinsii (Saff.) Seigler & Ebinger—Collins acacia
- Vachellia constricta (Benth.) Seigler & Ebinger—Whitethorn acacia, Mescat acacia
- Vachellia cookii (Saff.) Seigler & Ebinger—Cook acacia, cockspur acacia
- Vachellia cornigera (L.) Seigler & Ebinger—bullhorn wattle, bull's-horn acacia, bull-horn thorn, oxhorn acacia
- Vachellia cucuyo (Barneby & Zanoni) Seigler & Ebinger—Cucuyo acacia
- Vachellia curvifructa (Burkart) Seigler & Ebinger
- Vachellia daemon (Ekman & Urb.) Seigler & Ebinger—Camagüey acacia
- Vachellia davyi (N.E.Br.) Kyal. & Boatwr.—corky-bark acacia
- Vachellia ditricha (Pedley) Kodela
- Vachellia dolichocephala (Harms) Kyal. & Boatwr.
- Vachellia douglasica (Pedley) Kodela
- Vachellia drepanolobium (Harms ex Sjöstedt) P.J.H. Hurter—whistling thorn
- Vachellia dyeri (P.P.Swartz) Kyal. & Boatwr.[24]
- Vachellia eburnea (L.f.) P. Hurter & Mabb.
- Vachellia ebutsiniorum (P.J.H. Hurter) Kyal. & Boatwr.—Ebutsini acacia
- Vachellia edgeworthii (T.Anders.) Kyal. & Boatwr.
- Vachellia elatior (Brenan) Kyal. & Boatwr.
- subsp. elatior (Brenan) Kyal. & Boatwr.
- subsp. turkanae (Brenan) Kyal. & Boatwr.
- Vachellia erioloba (E.Mey.) P.J.H. Hurter—camel thorn (Kameeldoring)
- Vachellia erythrophloea (Brenan) Kyal. & Boatwr.
- Vachellia etbaica (Schweinf.) Kyal. & Boatwr.—savannah thorn
- subsp. australis (Brenan) Kyal. & Boatwr.
- subsp. etbaica (Schweinf.) Kyal. & Boatwr.
- subsp. platycarpa (Brenan) Kyal. & Boatwr.
- subsp. uncinata (Brenan) Kyal. & Boatwr.
- Vachellia exuvialis (Verdoorn) Kyal. & Boatwr.—flaky-bark acacia
- Vachellia farnesiana (L.) Wight & Arn.—huisache
- var. farnesiana (L.) Wight & Arn.
- var. guanacastensis (H.D.Clarke et al.) Wight & Arn.
- var. minuta (M.E.Jones) Wight & Arn.
- var. pinetorum (F.J.Herm.) Wight & Arn.—pineland wattle
- Vachellia fischeri (Harms) Kyal. & Boatwr.—flat-topped thorn
- Vachellia flava (Forssk.) Kyal. & Boatwr.
- Vachellia gentlei (Standley) Seigler & Ebinger—gentle acacia
- Vachellia gerrardii (Benth.) P.J.H. Hurter—red acacia
- var. calvescens (Brenan) P.J.H. Hurter
- var. gerrardii (Benth.) P.J.H. Hurter
- var. latisiliqua (Brenan) P.J.H. Hurter
- Vachellia glandulifera (S. Watson) Seigler & Ebinger
- Vachellia globulifera (Saff.) Seigler & Ebinger—globular acacia
- Vachellia grandicornuta (Gerstner) Seigler & Ebinger—horned-thorn acacia
- Vachellia guanacastensis (Clark, Seigler, & Ebinger) Seigler & Ebinger
- Vachellia gummifera (Willd.) Kyal. & Boatwr.—gum-bearing acacia
- Vachellia haematoxylon (Willd.) Seigler & Ebinger—gray camel thorn, giraffe thorn[25]
- Vachellia harmandiana (Pierre) Maslin, Seigler & Ebinger
- Vachellia hebeclada (DC.) Kyal. & Boatwr.—candle-pod acacia
- subsp. chobiensis (O.B.Miller) Kyal. & Boatwr.
- subsp. hebeclada (DC.) Kyal. & Boatwr.
- subsp. tristis (A.Schreiber) Kyal. & Boatwr.
- Vachellia hindsii (Benth.) Seigler & Ebinger—Hinds acacia
- Vachellia hockii (De Wild.) Seigler & Ebinger
- Vachellia horrida (L.) Kyal. & Boatwr.—long white-galled acacia
- subsp. benadirensis (Chiov.) Kyal. & Boatwr.
- subsp. horrida (L.) Kyal. & Boatwr.
- Vachellia hydaspica (J.R. Drumm. ex R. Parker) Ali
- Vachellia inopinata (Prain) Maslin, Seigler & Ebinger
- Vachellia insulae-iacobi (L. Riley) Seigler & Ebinger
- Vachellia jacquemontii (Benth.) ali—baonḷī, raati-banwali
- Vachellia janzenii (Ebinger & Seigler) Seigler & Ebinger—Janzen acacia
- Vachellia karroo (Hayne) Banfi & Galasso—Karroo Bush[24]
- Vachellia kingii (Prain) Maslin, Seigler & Ebinger
- Vachellia kirkii (Oliv.) Kyal. & Boatwr.—flood plain acacia
- subsp. kirkii (Oliv.) Kyal. & Boatwr.
- var. kirkii (Oliv.) Kyal. & Boatwr.
- var. sublaevis (Brenan) Kyal. & Boatwr.
- subsp. mildbraedii (Harms) Kyal. & Boatwr.
- subsp. kirkii (Oliv.) Kyal. & Boatwr.
- Vachellia koltermanii R. García, M. Mejía, Ebinger, & Seigler[26]
- Vachellia kosiensis (P.P.Sw. ex Coates Palgr.) Kyal. & Boatwr.[24]—dune acacia, dune sweet-thorn
- Vachellia lahai (Steud. & Hochst. ex. Benth.) Kyal. & Boatwr.—red-thorn acacia
- Vachellia lasiopetala (Oliv.) Kyal. & Boatwr.
- Vachellia latispina (J.E.Burrows & S.M.Burrows) Kyal. & Boatwr.
- Vachellia leucophloea (Roxb.) Maslin, Seigler & Ebinger—pilang
- var. leucophloea (Roxb.) Maslin, Seigler & Ebinger
- var. microcephala (Kurz) Maslin, Seigler & Ebinger
- Vachellia leucospira (Brenan) Kyal. & Boatwr.
- Vachellia luederitzii (Engl.) Kyal. & Boatwr.—bastard umbrella thorn
- var. luederitzii (Engl.) Kyal. & Boatwr.—Kalahari-sand acacia
- var. retinens (Sim) Kyal. & Boatwr.—balloon-thorn acacia
- Vachellia macracantha (Humb. & Bonpl. ex Willd.) Seigler & Ebinger—longspine acacia, French casha, long-spine acacia, porknut, cambrón, long-spined acacia, (Jamaica) parknut, (Virgin Islands) wild tamarind, (Netherlands Antilles) Creole casha, Spanish casha, steel acacia, (Virgin Islands) stink casha, strink casha
- Vachellia macrothyrsa (Harms) Kyal. & Boatwr.
- Vachellia malacocephala (Harms) Kyal. & Boatwr.—black-galled acacia
- Vachellia mayana (Lundell) Seigler & Ebinger—Maya Acacia
- Vachellia mbuluensis (Brenan) Kyal. & Boatwr.—hairy-galled acacia
- Vachellia melanoceras (Beurl.) Seigler & Ebinger—blackthorn acacia, bullhorn acacia
- Vachellia montana (P.P.Swartz) Kyal. & Boatwr.
- Vachellia myaingii (Lace) Maslin, Seigler & Ebinger
- Vachellia myrmecophila (R.Vig.) Boatwr.
- Vachellia natalitia (E.Mey.) Kyal. & Boatwr.[24]—pale-bark acacia, pale-bark sweet thorn
- Vachellia nebrownii (Burtt Davy) Seigler & Ebinger—water acacia, water thorn
- Vachellia negrii (Pichi-Sermolli) Kyal. & Boatwr.
- Vachellia nilotica (L.) P.J.H. Hurter & Mabb.—scented-pod acacia, gum Arabic tree, babul, Amrad gum, thorny mimosa of India
- subsp. adstringens (Schumach. & Thonn.) P.J.H. Hurter & Mabb.
- subsp. cupressiformis (J.L.Stewart) P.J.H. Hurter & Mabb.
- subsp. hemispherica (Ali & Faruqi) P.J.H. Hurter & Mabb.
- subsp. indica (Benth.) P.J.H. Hurter & Mabb.—Babul, Prickly acacia
- subsp. kraussiana (Benth.) P.J.H. Hurter & Mabb.
- subsp. leiocarpa (Brenan) P.J.H. Hurter & Mabb.
- subsp. nilotica (L.) P.J.H. Hurter & Mabb.
- subsp. subalata (Vatke) P.J.H. Hurter & Mabb.
- subsp. tomentosa (Benth.) P.J.H. Hurter & Mabb.
- Vachellia nubica (Benth.) Kyal. & Boatwr.
- Vachellia oerfota (Forssk) Kyal. & Boatwr.
- var. brevifolia (Boulos) Kyal. & Boatwr.
- var. oerfota (Forssk) Kyal. & Boatwr.
- Vachellia origena (Hunde) Kyal. & Boatwr.
- Vachellia ormocarpoides (P.J.H. Hurter) Kyal. & Boatwr.—Leolo thorn
- Vachellia oviedoensis (R. García & M. Mejía) Seigler & Ebinger
- Vachellia pacensis (Rudd & Carter) Seigler & Ebinger
- Vachellia pachyphloia (W. Fitzg.) Kodela
- subsp. brevipinnula (Tindale & Kodela) Kodela
- subsp. pachyphloia (W. Fitzg.) Kodela
- Vachellia pallidifolia (Tindale) Kodela
- Vachellia paolii (Chiov.) Kyal. & Boatwr.
- subsp. paolii (Chiov.) Kyal. & Boatwr.
- subsp. paucijuga (Brenan) Kyal. & Boatwr.
- Vachellia pennatula (Schltdl. & Cham.) Seigler & Ebinger—feather acacia
- var. parvicephala Seigler & Ebinger
- var. pennatula (Schltdl. & Cham.) Seigler & Ebinger
- Vachellia permixta (Burtt Davy) Kyal. & Boatwr.—slender acacia
- Vachellia pilispina (Pichi-Sermolli) Kyal. & Boatwr.—mpande
- Vachellia polypyrigenes (Greenm.) Seigler & Ebinger
- Vachellia prasinata (Hunde) Kyal. & Boatwr.
- Vachellia pringlei (Rose) Seigler & Ebinger—Pringle acacia
- var. californica —California Pringle acacia
- var. pringlei (Rose) Seigler & Ebinger—typical Pringle acacia
- Vachellia pseudofistula (Harms) Kyal. & Boatwr.—ant-galled acacia
- Vachellia qandalensis (Thulin) Kyal. & Boatwr.
- Vachellia quintanilhae (Torre) Kyal. & Boatwr.
- Vachellia reficiens (Wawra) Kyal. & Boatwr.—red-bark acacia
- subsp. misera (Vatke) Kyal. & Boatwr.
- subsp. reficiens (Wawra) Kyal. & Boatwr.
- Vachellia rehmanniana (Schinz) Kyal. & Boatwr.—silky acacia
- Vachellia rigidula (Benth.) Seigler & Ebinger—blackbrush acacia, blackbrush
- Vachellia robbertsei (P.P.Swartz) Kyal. & Boatwr.[24]—Sekhukhune acacia
- Vachellia robusta (Burch.) Kyal. & Boatwr.—splendid acacia
- subsp. clavigera (E.Mey.) Kyal. & Boatwr.—river acacia
- subsp. robusta (Burch.) Kyal. & Boatwr.—robust acacia
- subsp. usambarensis (Taub.) Kyal. & Boatwr.
- Vachellia roigii (Léon) Seigler & Ebinger—Roig acacia
- Vachellia rorudiana (Christopherson) Seigler & Ebinger—Galapagos acacia
- Vachellia ruddiae (D. H. Janzen) Seigler & Ebinger—Rudd acacia
- Vachellia schaffneri (S. Watson) Seigler & Ebinger—Schaffner's wattle, twisted acacia
- var. bravoensis (Isely) Seigler & Ebinger
- var. schaffneri (S. Watson) Seigler & Ebinger
- Vachellia schottii (Torr.) Seigler & Ebinger—Schott's wattle
- Vachellia sekhukhuniensis (P.J.H. Hurter) Kyal. & Boatwr.—Sekhukhune thorn
- Vachellia seyal (Delile) P.J.H. Hurter—white whistling thorn
- var. fistula (Schweinf.) P.J.H. Hurter
- var. seyal (Delile) P.J.H. Hurter
- Vachellia siamensis (Craib) Maslin, Seigler & Ebinger
- Vachellia sieberiana (DC.) Kyal. & Boatwr.—paperbark acacia, paperbark thorn
- var. sieberiana (DC.) Kyal. & Boatwr.
- var. villosa (A.Chev.) Kyal. & Boatwr.
- var. woodii (Burtt Davy) Kyal. & Boatwr.
- Vachellia sphaerocephala (Schltdl. & Cham.) Seigler & Ebinger—roundhead acacia, bee wattle
- Vachellia stuhlmannii (Taub.) Kyal. & Boatwr.—olive-barked thorn, vlei acacia
- Vachellia suberosa (A. Cunn. ex Benth.) Kodela—corkybark wattle
- Vachellia sutherlandii (F. Muell.) Kodela—corkwood wattle
- Vachellia swazica (Burtt Davy) Kyal. & Boatwr.—Swazi acacia
- Vachellia tenuispina (Verdoorn) Kyal. & Boatwr.—turf acacia
- Vachellia tephrophylla (Thulin) Kyal. & Boatwr.
- Vachellia theronii (P.P.Sw.) Boatwr.[24]—slender mountain thorn
- Vachellia tomentosa (Rottler) Maslin, Seigler & Ebinger—klampis
- Vachellia torrei (Brenan) Kyal. & Boatwr.—Mozambique sticky thorn
- Vachellia tortilis (Forssk.) Galasso & Banfi—umbrella thorn, umbrella acacia
- subsp. heteracantha (Burch.) Galasso & Banfi
- subsp. raddiana (Savi) Galasso & Banfi
- var. pubescens (A.Chev.) Galasso & Banfi
- var. raddiana (Savi) Galasso & Banfi
- subsp. spirocarpa (Hochst. ex A.Rich.) Galasso & Banfi
- var. crinita (Chiov.) Galasso & Banfi
- var. spirocarpa (Hochst. ex. A.Rich.) Galasso & Banfi
- subsp. tortilis (Forssk.) Galasso & Banfi
- Vachellia tortuosa (L.) Seigler & Ebinger—twisted acacia, acacia bush, casia, catclaw, Dutch casha, huisachillo, Rio Grande acacia, sweet briar, sweet-briar, wild poponax
- Vachellia turnbulliana (Brenan) Kyal. & Boatwr.—velvet pod acacia
- Vachellia valida (Tindale & Kodela) Kodela
- Vachellia vernicosa (Britton & Rose) Seigler & Ebinger—viscid acacia
- Vachellia viguieri (Villiers & Du Puy) Boatwr.
- Vachellia villaregalis (McVaugh) Seigler & Ebinger
- Vachellia walwalensis (Gilliland) Kyal. & Boatwr.
- Vachellia xanthophloea (Benth.) P.J.H. Hurter—fever tree
- Vachellia zanzibarica (S.Moore) Kyal. & Boatwr.—coastal whistling thorn
- var. microphylla (Brenan) Kyal. & Boatwr.
- var. zanzibarica (S.Moore) Kyal. & Boatwr.
- Vachellia zapatensis (Urb. & Ekman) Seigler & Ebinger
Incertae sedis
These species are suspected to belong to Vachellia, but have not been formally transferred.[18]
- Acacia callicoma Meisn.
- Acacia harala Thulin & Gifri
- Acacia hunteri Oliv.
- Acacia johnwoodii Boulos
- Acacia planifrons Koenig ex Wight & Arn.
- Acacia pseudo-eburnea J.R. Drumm. ex Dunn
- Acacia tanjorensis Ragup., Thoth. & Mahad.
- Acacia yemenensis Boulos
Hybrids
- Vachellia × cedilloi (Rico Arce) Seigler & Ebinger
- Vachellia campechiana × pennatula
- Vachellia erioloba × haematoxylon
- Vachellia × gladiata (Saff.) Seigler & Ebinger
- Vachellia kirkii × seyal
- Vachellia macracantha × pennatula
- Vachellia seyal var. fistula × xanthophloea
- Vachellia × standleyi (Saff.) Seigler & Ebinger
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Maslin, B. R.; Orchard, A. E.; West, J. G.. "Nomenclatural and classification history of Acacia (Leguminosae: Mimosoideae), and the implications of generic subdivision". http://worldwidewattle.com/infogallery/taxonomy/nomen-class.pdf.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "Phylogenetic position and revised classification of Acacia s.l. (Fabaceae: Mimosoideae) in Africa, including new combinations in Vachellia and Senegalia.". Botanical Journal of the Linnean Society 172 (4): 500–523. 2013. doi:10.1111/boj.12047.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "Taxonomic Revision of the Vachellia acuifera Species Group (Fabaceae: Mimosoideae) in the Caribbean". Systematic Botany 34 (1): 84–101. 2009. doi:10.1600/036364409787602285.
- ↑ Dyer C. (2014). "New names for the African Acacia species in Vachellia and Senegalia". Southern Forests: A Journal of Forest Science 76 (4): iii. doi:10.2989/20702620.2014.980090.
- ↑ Austin, Daniel F. (2004). Florida ethnobotany Fairchild Tropical Garden, Coral Gables, Florida, Arizona-Sonora Desert Museum, Tucson, Arizona: with more than 500 species illustrated by Penelope N. Honychurch ... [et al.]. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press. pp. 58–59. ISBN 9780203491881.
- ↑ Shorrocks, Bryan; Bates, William (2014). The Biology of African Savannahs (Biology of Habitats Series ed.). Oxford University Press. pp. 231–233. ISBN 978-0198702702.
- ↑ Chidumayo, Emmanuel N.; Gumbo, Davison J. (2010). The Dry Forests and Woodlands of Africa: Managing for Products and Services. Routledge. p. 25. ISBN 9781136531378.
- ↑ Corder, Hugh; Glazewski, Jan; Bleazard, Janice (2009). A Rose is a Rose but is an 'Acacia' an 'Acacia'? Global administrative law: development and innovation. Cape Town: Juta. ISBN 9780702181900.
- ↑ Moore, Gerry; Smith, Gideon F.; Figueiredo, Estrela; Demissew, Sebsebe; Lewis, Gwilym; Schrire, Brian; Rico, Lourdes; van Wyk, Abraham E. et al. (June 2011). "The Acacia controversy resulting from minority rule at the Vienna Nomenclature Section: Much more than arcane arguments and complex technicalities". Taxon 60 (3): 852–857. doi:10.1002/tax.603017. http://www.iapt-taxon.org/historic/Congress/IBC_2011/Acacia_not_pragm.pdf. Retrieved 19 May 2016.
- ↑ "The Acacia debate". IBC2011 Congress News. http://worldwidewattle.com/infogallery/nomenclature/nameissue/melbourne-ibc-2011-congress-news-tuesday-26-july.pdf.
- ↑ "Conserving Acacia Mill. with a conserved type: What happened in Melbourne?". Taxon. http://www.iapt-taxon.org/historic/Congress/IBC_2011/Acacia_happen2.pdf.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 Hyde, Mark. "3446.000 Acacia Mill.—Thorn trees". http://www.zimbabweflora.co.zw/speciesdata/genus.php?genus_id=667.
- ↑ "Handbook on seeds of dry-zone acacias, 3. Reproductive biology". FAO Corporate Document Repository: Agriculture and Consumer Protection. http://www.fao.org/docrep/006/q2190e/Q2190E03.htm.
- ↑ Thiele KR. (2011). "The controversy over the retypification of Acacia Mill. with an Australian type: A pragmatic view". Taxon 60 (1): 194–198. doi:10.1002/tax.601017. http://www.iapt-taxon.org/historic/Congress/IBC_2011/Acacia_pragm.pdf.
- ↑ "New combinations in the genus Vachellia (Fabaceae: Mimosoideae) from the New World". Phytologia 87 (3): 139–78. 2005. http://biostor.org/reference/63157.
- ↑ "New combinations in Senegalia and Vachellia (Fabaceae: Mimosoideae)". Phytologia 92 (1): 92–95. 2010. http://www.phytologia.org/uploads/2/3/4/2/23422706/92192-95seaglernewcombinations.pdf.
- ↑ "New combinations in Senegalia and Vachellia (Leguminosae: Mimosoideae) for Southeast Asia and China.". Blumea 58 (1): 39–44. 2013. doi:10.3767/000651913X669914. http://www.repository.naturalis.nl/record/524646.
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 Maslin B. "List of Acacia sensu lato species". http://www.worldwidewattle.com/speciesgallery/home.php.
- ↑ "New combinations in the genus Vachellia (Fabaceae: Mimosoideae) from Australia". Telopea 11 (2): 233–244. 2006. doi:10.7751/telopea20065723.
- ↑ Ali SI. (2014). "The Genus Acacia s.l. in Pakistan". Pak J Bot 46 (1): 1–4. https://www.pakbs.org/pjbot/PDFs/46(1)/01.pdf.
- ↑ "Phylogenetic position of Madagascan species of Acacia s.l. and new combinations in Senegalia and Vachellia (Fabaceae, Mimosoideae, Acacieae)". Bot J Linn Soc 179 (2): 288–294. 2015. doi:10.1111/boj.12320.
- ↑ Maiden, J. H. (1889). The Useful Native Plants of Australia (including Tasmania). Sydney: Turner and Henderson. p. 3.
- ↑ Maslin BR. (2014). "Vachellia bolei (Fabaceae: Mimosoideae), the correct name for a species from India". Nuytsia 24: 21–22. https://florabase.dpaw.wa.gov.au/science/nuytsia/708.pdf.
- ↑ 24.0 24.1 24.2 24.3 24.4 24.5 Taxon in the V. karroo complex, see: Roland, Dr. Wolf-Achim. "The Acacia (s.l.)-karroo complex, Status 2014". http://www.acacia-world.net/index.php/africa-me/south-africa/the-vachellia-karroo-complex.
- ↑ "Protected Trees". Department of Water Affairs and Forestry, Republic of South Africa. 3 May 2013. http://www2.dwaf.gov.za/dwaf/cmsdocs/4116___poster%20protected%20trees.pdf.
- ↑ "A new species of Vachellia (Fabaceae: Mimosoideae) from Haiti". Journal of the Botanical Research Institute of Texas 6 (1): 45. 2012. http://connection.ebscohost.com/c/articles/78422251/new-species-vachellia-fabaceae-mimosoideae-from-haiti.
Wikidata ☰ Q956173 entry
 |


