Biology:Wedge-billed woodcreeper
| Wedge-billed woodcreeper | |
|---|---|

| |
| at Rio Silanche (PVM), NW Ecuador | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Passeriformes |
| Family: | Furnariidae |
| Subfamily: | Dendrocolaptinae |
| Genus: | Glyphorynchus Wied-Neuwied, 1831 |
| Species: | G. spirurus
|
| Binomial name | |
| Glyphorynchus spirurus (Vieillot, 1819)
| |
| |
| Synonyms | |
| |
The wedge-billed woodcreeper (Glyphorynchus spirurus) is a sub-oscine passerine bird in subfamily Dendrocolaptinae of the ovenbird family Furnariidae. It is found in Mexico, Central America, Brazil, Bolivia, Ecuador, French Guiana, Guyana, Peru, Suriname, and Venezuela.[2]
Taxonomy and systematics
The wedge-billed woodcreeper is the only member of its genus. It has these 13 subspecies that are sorted into three groups and a species by the Clements taxonomy:[2][3]
"pectoralis" group
- G. s. pectoralis Sclater, PL & Salvin, 1860
- G. s. subrufescens Todd, 1948
- G. s. pallidulus Wetmore, 1970
- G. s. integratus Zimmer, JT, 1946
"spirurus" group
- G. s. rufigularis Zimmer, JT, 1934
- G. s. amacurensis Phelps, WH & Phelps, WH Jr, 1952
- G. s. spirurus (Vieillot, 1819)
- G. s. coronobscurus Phelps, WH & Phelps, WH Jr, 1955
- G. s. castelnaudii des Murs, 1856
"'albigularis"
- G. s. albigularis Chapman, 1923
"cuneatus" group
- G. s. inornatus Zimmer, JT, 1934
- G. s. paraensis Pinto, 1974
- G. s. cuneatus (Lichtenstein, MHC, 1820)
The groups differ vocally; that and plumage and genetic differences among the subspecies suggest that the wedge-billed woodcreeper is actually more than one species.[4][5]
Description
The wedge-billed woodcreeper is the smallest woodcreeper, with a short, upturned, wedge-shaped bill resembling those of the three members of genus Xenops. It is 13 to 16 cm (5.1 to 6.3 in) long and weighs 10.5 to 21 g (0.37 to 0.74 oz). The sexes are alike. The nominate subspecies G. s. spirurus has a grayish forehead, a rich brown to russet-brown crown and nape, light buff lores, a thin buff to buff-white supercilium, a buff eyering, sooty-brown auriculars, and a brown malar stripe. Its upper back and scapulars are rich brown to russet-brown, and its lower back, uppertail coverts, and tail are cinnamon-rufous to rufous-chestnut. Its wing coverts are russet, its inner secondaries rufous, and its other secondaries and its primaries dark brown with blackish tips. The underside of most wing feathers have a stripe of buff to buff-white that shows as a band in flight. The sides of its neck are brown with small buff spots and its throat is whitish buff to buff with some dusky spots. Its underparts are olive-brown to russet-brown, its undertail coverts have a rufous-chestnut wash, and its underwing coverts and axillaries are white. Its upper breast has large round fulvous spots and its lower breast has narrow streaks of the same color. Its iris is dark brown to amber, its bill black with a gray base to the mandible, and its legs and feet pinkish gray, dark gray, dark greenish, or brownish black.[5]
The other subspecies of the wedge-billed woodcreeper differ from the nominate thus:[5]
- G. s. pectoralis, darker and more olivaceous underparts, cinnamon-buff throat, triangle markings on breast
- G. s. subrufescens, intermediate between pectoralis and pallidulus with little streaking on breast
- G. s. pallidulus, like pectoralis but paler overall
- G. s. integratus, paler than subrufescens, pale buff throat
- G. s. rufigularis, deep rufous throat, darker ochraceous wing band, less olive underparts than castelnaudii
- G. s. amacurensis, paler and yellowish throat, more olivaceous crown and underparts, browner back
- G. s. coronobscurus, like rufigularis but with darker dusky brown crown and more olivaceous underparts
- G. s. castelnaudii, darker and more olivaceous underparts
- G. s. albigularis, narrower whitish throat and breast spots
- G. s. inornatus, paler and buffier throat, browner spotting on throat, browner and unmarked belly
- G. s. paraensis, like cuneatus but more olive-brown, rufescent tinge to throat markings
- G. s. cuneatus, browner upperparts, paler throat with heavy markings
Several of the subspecies intergrade in their contact zones, making assignment of some sub-populations to a subspecies difficult.[5]
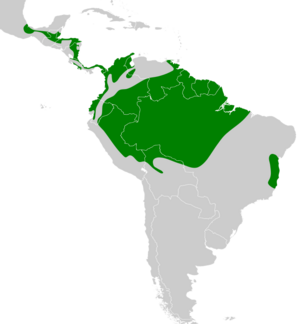
Distribution and habitat
The subspecies of the wedge-billed woodcreeper are found thus:[2][3][5]
- G. s. pectoralis, from Veracruz in southern Mexico south on the Caribbean slope through Belize, Guatemala, Honduras, and Nicaragua onto the Caribbean and Pacific slopes through Costa Rica into central and western Panama. At least one record from El Salvador.[6]
- G. s. subrufescens, Pacific slope of southeastern Panama south through western Colombia into western Ecuador as far as El Oro Province
- G. s. pallidulus, both slopes of eastern Panama into Colombia's Chocó Department
- G. s. integratus, northern Colombia and east of its Andes into western Venezuela
- G. s. rufigularis, the Amazon Basin north of the Amazon River from central Colombia and southern Venezuela south into northeastern Ecuador and northwestern Brazil east to the Rio Negro
- G. s. amacurensis, northeastern Venezuela's Sucre and Delta Amacuro states
- G. s. spirurus, the Amazon Basin north of the Amazon River from eastern Venezuela east through the Guianas and Brazil from the Rio Negro to the Atlantic Ocean
- G. s. coronobscurus, Cerro de la Neblina in southern Venezuela
- G. s. castelnaudii, the Amazon Basin south of the Rio Napo and Amazon River from eastern and northeastern Peru into Brazil east to the Rio Madeira
- G. s. albigularis, the Amazon Basin in southeastern Peru and northern Bolivia
- G. s. inornatus, the Amazon Basin south of the Amazon River in Brazil between the Rio Madeira and the Rio Tapajós south to Mato Grosso and northeastern Bolivia
- G. s. paraensis, the Amazon Basin south of the Amazon River in Brazil between the Rio Tapajós and the Atlantic Ocean
- G. s. cuneatus, coastal eastern Brazil between the states of Bahia and Espírito Santo
The wedge-billed woodcreeper primarily inhabits tropical evergreen forest including rainforest and to a lesser extent the lower reaches of montane evergreen forest. It favors the interior of mature primary forest and also occurs at the forest edge and in mature secondary forest. It occasionally is found in bamboo, young secondary forest, plantations, and open areas with some trees. In Amazonia it mostly occurs in terra firme and floodplains, and less often in gallery forest, palm swamps, and seasonally flooded forest like várzea. In northern Central America it reaches an elevation of 1,350 m (4,400 ft), in Costa Rica 1,500 m (4,900 ft), in Panama and Colombia 2,100 m (6,900 ft), in Venezuela 1,800 m (5,900 ft), in Ecuador 1,700 m (5,600 ft), and in Brazil 1,200 m (3,900 ft).[5][7][8][9][10][11]
Behavior
Movement
The wedge-billed woodcreeper is mostly a year-round resident throughout its range. There is some evidence of elevational movement in Costa Rica.[5]
Feeding
The wedge-billed woodcreeper usually forages in pairs or as a member of mixed-species feeding flocks, especially those led by Thamnomanes antshrikes. It seldom follows army ant swarms but will feed at the edges of them when a feeding flock encounters a swarm. It mostly feeds in the lower to middle levels of the forest though it will go higher. Its diet is almost entirely very small arthropods, which it captures while hitching up a trunk or less often along a branch. It picks prey from crevices and clumps of moss, flakes bark, and hammers on wood.[5][9][10]
Breeding
The wedge-billed woodcreeper's breeding season varies geographically; examples are a March to June season in Costa Rica and both September to December and February to June in Amazonian Brazil. It builds a cup nest of fine plant fibers in a cavity, usually natural but sometimes made by a woodpecker. Cavities have been found in tree trunks and stumps; cavities in vine tangles, between root butresses, and under dead palm fronds are also used. Nests are normally within 6 m (20 ft) of the ground and usually much lower. The clutch size is two eggs. The incubation period is not known; fledging occurs about 17 days after hatch. Both parents incubate the eggs and brood and provision nestlings.[5]
Vocalization
The wedge-billed woodcreeper sings mostly at dusk and dawn, though occasionally during the day as well. The subspecies in the pectoralis group of Central America into Colombia sing "a rapidly ascending, accelerating and somewhat slurred series of c. 25 bubbly notes...'twee-lee-lee-le-le-ee-ee-eeeeeé' ". It is also described as "weet-weet-WEEET-WEEET-weet-peet-peeet't't't't't't'teu". In northern and western Amazonia the song is "a series of relatively clear whistles that ascends more slowly...'too-e too-e tu-tu-tu-tue’tue’twu’tweetwee' " or "tuee-tuee-tuee-tuee-teeé-teeé-tueé?". Birds in the southeastern part of the range sing "2 short, clear whistles in with second note somewhat lower in frequency than first, 'treeee, treep' " or "weep-weep". The species' calls vary less among the subspecies, and include "pweek!", "cheeyf!", "chiff!", "schip", "ksh", "psieh", and "djeep".[5][7][10][11]
Status
The IUCN has assessed the wedge-billed woodcreeper as being of Least Concern. It has a very large range and an estimated population of at least 500,000 mature individuals, though that number is believed to be decreasing. No immediate threats have been identified.[1] In much of its range it is considered fairly common to common, though uncommon in much of northern Central America. The isolated subspecies G. s. cuneatus is also uncommon and little of its Atlantic Forest habitat remains. Its "ability to survive in second growth and forest fragments at many sites suggests a lower degree of sensitivity to habitat disturbance than is true of most woodcreepers" but there appears to be some reduction in density in disturbed forest.[5]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 BirdLife International (2020). "Wedge-billed Woodcreeper Glyphorynchus spirurus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2020: e.T22703043A140070412. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-3.RLTS.T22703043A140070412.en. https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/22703043/140070412. Retrieved 28 May 2023.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Gill, Frank; Donsker, David; Rasmussen, Pamela, eds (January 2023). "Ovenbirds, woodcreepers". https://www.worldbirdnames.org/new/bow/ovenbirds/.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Clements, J. F., T. S. Schulenberg, M. J. Iliff, T. A. Fredericks, J. A. Gerbracht, D. Lepage, S. M. Billerman, B. L. Sullivan, and C. L. Wood. 2022. The eBird/Clements checklist of birds of the world: v2022. Downloaded from https://www.birds.cornell.edu/clementschecklist/download/ retrieved November 10, 2022
- ↑ Remsen, J. V., Jr., J. I. Areta, E. Bonaccorso, S. Claramunt, A. Jaramillo, D. F. Lane, J. F. Pacheco, M. B. Robbins, F. G. Stiles, and K. J. Zimmer. Version 30 January 2023. A classification of the bird species of South America. American Ornithological Society. https://www.museum.lsu.edu/~Remsen/SACCBaseline.htm retrieved January 30, 2023
- ↑ 5.00 5.01 5.02 5.03 5.04 5.05 5.06 5.07 5.08 5.09 5.10 Marantz, C. A., A. Aleixo, L. R. Bevier, M. A. Patten, and D. A. Christie (2020). Wedge-billed Woodcreeper (Glyphorynchus spirurus), version 1.0. In Birds of the World (J. del Hoyo, A. Elliott, J. Sargatal, D. A. Christie, and E. de Juana, Editors). Cornell Lab of Ornithology, Ithaca, NY, USA. https://doi.org/10.2173/bow.webwoo1.01 retrieved May 28, 2023
- ↑ Herrera, Néstor; Rivera, Roberto; Ibarra Portillo, Ricardo & Rodríguez, Wilfredo (2006): Nuevos registros para la avifauna de El Salvador. ["New records for the avifauna of El Salvador"]. Boletín de la Sociedad Antioqueña de Ornitología 16(2): 1-19. [Spanish with English abstract]PDF fulltext
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Fagan, Jesse; Komar, Oliver (2016). Field Guide to Birds of Northern Central America. Peterson Field Guides. Boston: Houghton Mifflin Harcourt. pp. 106. ISBN 978-0-544-37326-6.
- ↑ Garrigues, Richard; Dean, Robert (2007). The Birds of Costa Rica. Ithaca: Zona Tropical/Comstock/Cornell University Press. p. 170. ISBN 978-0-8014-7373-9.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 McMullan, Miles; Donegan, Thomas M.; Quevedo, Alonso (2010). Field Guide to the Birds of Colombia. Bogotá: Fundación ProAves. pp. 124. ISBN 978-0-9827615-0-2.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 Ridgely, Robert S.; Greenfield, Paul J. (2001). The Birds of Ecuador: Field Guide. II. Ithaca: Cornell University Press. pp. 380. ISBN 978-0-8014-8721-7.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 van Perlo, Ber (2009). A Field Guide to the Birds of Brazil. New York: Oxford University Press. pp. 200. ISBN 978-0-19-530155-7.
Further reading
- Skutch, Alexander F. (1969). "Wedge-billed woodcreeper". Life Histories of Central American Birds III: Families Cotingidae, Pipridae, Formicariidae, Furnariidae, Dendrocolaptidae, and Picidae. Pacific Coast Avifauna, Number 35. Berkeley, California: Cooper Ornithological Society. pp. 392–395. https://sora.unm.edu/sites/default/files/journals/pca/pca_035.pdf#page=392.
- Hilty, Steven L. (2003): Birds of Venezuela. Christopher Helm, London. ISBN:0-7136-6418-5
- Stiles, F. Gary & Skutch, Alexander Frank (1989): A guide to the birds of Costa Rica. Comistock, Ithaca. ISBN:0-8014-9600-4
Wikidata ☰ Q744905 entry
 |


