Biology:Yellow-bellied flycatcher
| Yellow-bellied flycatcher | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Passeriformes |
| Family: | Tyrannidae |
| Genus: | Empidonax |
| Species: | E. flaviventris
|
| Binomial name | |
| Empidonax flaviventris (Baird, WM & Baird, SF, 1843)
| |
| |
The yellow-bellied flycatcher (Empidonax flaviventris) is a small insect-eating bird of the tyrant flycatcher family.
Description
Adults have greenish upperparts and yellowish underparts (especially on the throat), with a dusky wash on the chest. They have a white or yellow eye ring that lacks the teardrop projection of Pacific-slope (E. difficilis) or cordilleran (E. occidentalis) flycatchers, white or yellowish wing bars that contrast strongly against the black wings, a broad, flat bill, and a relatively short tail when compared to other members of the genus. The upper mandible of the bill is dark, while the lower mandible is orange-pink. DNA testing in 2014 confirmed a field mark, involving the extent of buffy edging on the secondaries, to reliably distinguish this species from the two so-called "Western Flycatchers."[2][3]
Measurements:[4]
- Length: 5.1–5.9 in (13–15 cm)
- Weight: 0.3–0.6 oz (8.5–17.0 g)
- Wingspan: 7.1–7.9 in (18–20 cm)
Yellow-bellied flycatchers wait on a perch low or in the middle of a tree and fly out to catch insects in flight, sometimes hovering over foliage. They sometimes eat berries or seeds.
File:Empidonax flaviventris - Yellow-bellied Flycatcher XC134691.ogg
The yellow-bellied flycatcher's song can be transcribed as a rough, descending "tse-berk", which can be similar to the more common least flycatcher's snappier, more evenly pitched "che-bek."
Breeding
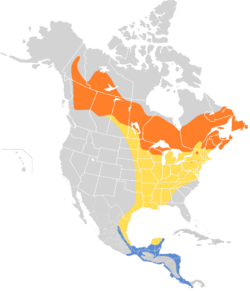
Their breeding habitat is wet northern woods, especially spruce bogs, across Canada and the northeastern United States. They make a cup nest in sphagnum moss on or near the ground.
Migration
These birds migrate to southern Mexico and Central America.
References
- ↑ BirdLife International (2016). "Empidonax flaviventris". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2016: e.T22699839A93750697. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22699839A93750697.en. https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/22699839/93750697. Retrieved 19 November 2021.
- ↑ Engel, Joshua (26 November 2014). "A first for Illinois, discovered in The Field Museum's collection". Field Museum of Natural History. https://www.fieldmuseum.org/blog/first-illinois-discovered-field-museums-collection.
- ↑ Engel, Joshua (2 December 2014). "Follow up: A first for Illinois, discovered in the Field Museum's collection". Field Museum of Natural History. https://www.fieldmuseum.org/blog/follow-first-illinois-discovered-field-museums-collection.
- ↑ "Yellow-bellied Flycatcher Identification, All About Birds, Cornell Lab of Ornithology" (in en). https://www.allaboutbirds.org/guide/Yellow-bellied_Flycatcher/id.
External links
- Yellow-bellied Flycatcher Species Account - Cornell Lab of Ornithology
- Yellow-bellied Flycatcher - Empidonax flaviventris - USGS Patuxent Bird Identification InfoCenter
- Yellow-bellied Flycatcher, Environment Canada
- Yellow-bellied Flycatcher Canadian range, Canadian Biodiversity Web Site
- "Yellow-bellied Flycatcher media". Internet Bird Collection. http://www.hbw.com/ibc/species/yellow-bellied-flycatcher-empidonax-flaviventris.
- Yellow-bellied Flycatcher photo gallery at VIREO (Drexel University)
Wikidata ☰ Q1062634 entry
 |



