Chemistry:1,2-Butylene carbonate
From HandWiki
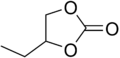
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
4-Ethyl-1,3-dioxolan-2-one | |
| Other names
1,2-Butanediol carbonate
2-Oxo-4-ethyl-1,3-dioxolane | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C5H8O3 | |
| Molar mass | 116.116 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
1,2-Butylene carbonate is an organic compound with formula C5H8O3, or (H5C2)(C2H3)(CO3). It is a double ester with the carbonate functional group bonded to both free ends of the 1,2-butylene group. It is also a heterocyclic compound with a five-membered ring, and can be seen as a derivative of dioxolane, specifically 4-ethyl-1,3-dioxolan-2-one.
1,2-Butylene carbonate is a polar aprotic solvent, which has been considered for electric battery applications (as a cheaper alternative to ionic liquids) and many other uses.[1]
See also
- Propylene carbonate
- trans-1,3-Butylene carbonate
References
- ↑ Jacek Kumełan, Dirk Tuma, Sergey P. Verevkin and Gerd Maurer (2008), Solubility of Hydrogen in the Cyclic Alkylene Ester 1,2-Butylene Carbonate. J. Chem. Eng. Data, 2008, 53 (12), pp 2844–2850. doi:10.1021/je800583r.
 |

