Chemistry:1,2-Diaminocyclohexane
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Cyclohexane-1,2-diamine | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 2735 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H14N2 | |
| Molar mass | 114.192 g·mol−1 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |  
|
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
| H302, H312, H314, H317, H318, H332, H335 | |
| P260, P261, P264, P270, P271, P272, P280, P301+312, P301+330+331, P302+352, P303+361+353, P304+312, P304+340, P305+351+338, P310, P312, P321, P322, P330, P333+313, P363, P403+233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
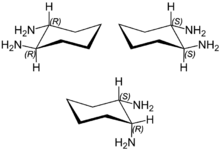
1,2-Diaminocyclohexane is an organic compound with the formula (CH2)4(CHNH2)2. It is a mixture of three stereoisomers: cis-1,2-diaminocyclohexane and both enantiomers of trans-1,2-diaminocyclohexane. The mixture is a colorless, corrosive liquid, although older samples can appear yellow. It is often called DCH-99 and also DACH.
Manufacture
The product is available commercially, manufactured by the hydrogenation of o-phenylenediamine. The two trans enantiomers can be resolved by conversion to diastereomeric salts of various chiral acids.[1]
Uses
The product is an epoxy curing agent for use in Coatings, Adhesives, Sealants and Elastomers - CASE.[2] It is particularly useful in epoxy flooring.[3] It may also be reacted with diethyl maleate utilizing the Michael reaction to produce a polyaspartic compound of CAS number 481040-92-0.[4] It may also be used in lubricants.[5] The product is also advertised as being useful as a chelating agent in a variety of applications including oil production.[6] It also is used in downfield oil and gas wells where there is an acidic stream to prevent corrosion to the bore piles.[7]
See also
References
- ↑ Kouklovsky, Cyrille; Langlois, Yves; Aguilar, Enrique; Fernández-García, Jesús M.; Sikervar, Vikas (2014). "(1S,2S)-1,2-Diaminocyclohexane" (in en). (1S,2S)-1,2-Diaminocyclohexane. pp. 1–23. doi:10.1002/047084289x.rn00145.pub3. ISBN 978-0-470-84289-8.
- ↑ "Dytek DCH-99 by INVISTA - Paint & Coatings". https://www.ulprospector.com/en/la/Coatings/Detail/25290/557016/Dytek-DCH-99.
- ↑ "A New Epoxy Curing Agent with Long Pot Life and Fast Cure" (in en). https://www.pcimag.com/articles/96269-a-new-epoxy-curing-agent-with-long-pot-life-and-fast-cure?v=preview.
- ↑ "Dytek DCH-99 | 1,2-Diaminocyclohexane" (in en-US). https://dytek.invista.com/products/dytek-dch-99/.
- ↑ "US Patent for Non-aromatic based antioxidants for lubricants Patent (Patent # 9,273,266 issued March 1, 2016) - Justia Patents Search". https://patents.justia.com/patent/9273266.
- ↑ "Technical Data Sheet Dytek DCH 99". https://dytek.invista.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/07/Dytek%E2%94%AC%C2%AB-DCH-99-12-Diaminocyclohexane-Technical-Data-Sheet.pdf.
- ↑ Materials, Ascend. "FlexaTram-DAM" (in en). https://www.ascendmaterials.com/products/specialty-chemicals/flexatram-amines/flexatram-dam/.
External links
 |
