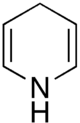
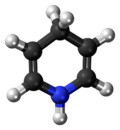
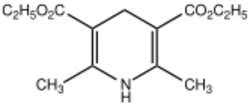
Chemistry:1,4-Dihydropyridine
|
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1,4-Dihydropyridine[1] | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
| MeSH | 1,4-dihydropyridine | ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C5H7N | |||
| Molar mass | 81.1158 g mol−1 | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
1,4-Dihydropyridine (DHP) is an organic compound with the formula CH2(CH=CH)2NH. The parent compound is uncommon,[2] but derivatives of 1,4-dihydropyridine are important commercially and biologically. The pervasive cofactors NADH and NADPH are derivatives of 1,4-dihydropyridine. 1,4-Dihydropyridine-based drugs are L-type calcium channel blockers, used in the treatment of hypertension. 1,2-Dihydropyridines are also known.[3][4]
Properties and reactions
A recurring feature of 1,4-dihydropyridines is the presence of substituents at the 2- and 6-positions. Dihydropyridines are enamines, which otherwise tend to tautomerize or hydrolyze.[citation needed]
The dominant reaction of dihydropyridines is their ease of oxidation. In the case of dihydropyridines with hydrogen as the substituent on nitrogen, oxidation yields pyridines:
- CH2(CH=CR)2NH → C5H3R2N + H2
The naturally-occurring dihydropyridines NADH and NADPH contain N-alkyl groups. Therefore, their oxidation does not yield pyridine, but N-alkylpyridinium cations:
- CH2(CH=CR)2NR' → C5H3R2NR' + H−
See also
- Dihydropyridine calcium channel blockers
- Hantzsch ester[5]
- Dihydropyridine receptor
References
- ↑ "1,4-dihydropyridine - Compound Summary". Pubchem Compound. US: National Center for Biotechnology Information. 27 March 2005. Identification and Related Records. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/summary/summary.cgi?cid=104822&loc=ec_rcs.
- ↑ Duburs, Gunãrs; Sausins, Alvils (1988). "Synthesis of 1,4-Dihydropyridines by Cyclocondensation Reactions". Heterocycles 27: 269. doi:10.3987/REV-87-370.
- ↑ Stout, David M.; Meyers, A. I. (1982). "Recent advances in the chemistry of dihydropyridines". Chemical Reviews 82 (2): 223–243. doi:10.1021/cr00048a004.
- ↑ Lavilla, Rodolfo (2002). "Recent developments in the chemistry of dihydropyridines". Journal of the Chemical Society, Perkin Transactions 1 (9): 1141–1156. doi:10.1039/B101371H.
- ↑ Cheung, Lawrence L. W.; Styler, Sarah A.; Dicks, Andrew P. (2010). "Rapid and Convenient Synthesis of the 1,4-Dihydropyridine Privileged Structure". Journal of Chemical Education 87 (6): 628–630. doi:10.1021/ed100171g. Bibcode: 2010JChEd..87..628C.
External links
- Dihydropyridines at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
 |