Chemistry:1,4-Diisocyanobutane
From HandWiki
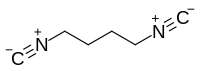
| |||
|
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1,4-diisocyanobutane | |||
| Systematic IUPAC name
1,4-diisocyanobutane | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C6H8N2 | |||
| Molar mass | 108.144 g·mol−1 | ||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS pictograms |  [1] [1]
| ||
| GHS Signal word | Danger[1] | ||
| H301, H311, H331[1] | |||
| P261, P264, P270, P271, P280, P301+316Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, P302+352, P304+340, P316Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, P321, P330, P361+364Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, P403+233, P405, P501[1] | |||
| Related compounds | |||
Related compounds
|
|||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Tracking categories (test):
1,4-Diisocyanobutane is an organic compound. Its structural formula is CN(CH2)4NC, which similar to adiponitrile but with carbon and nitrogen of cyanide groups switching places. It has been used as a ligand in the formation of organometallic complexes, such as with rhodium - [Rh2(CNC8H14NC)4]2+.[2]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 PubChem. "1,4-Diisocyanobutane" (in en). https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/4233940.
- ↑ Yaneff, P.V.; Powell, J. (1979). "Dinuclear complexes of rhodium(I) containing diisocyanide ligands and some of their phosphine derivatives". Journal of Organometallic Chemistry 179: 101–113. doi:10.1016/S0022-328X(00)87800-6.
 |



