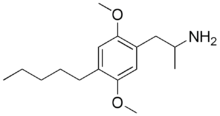
Chemistry:2,5-Dimethoxy-4-amylamphetamine
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1-(2,5-Dimethoxy-4-pentylphenyl)propan-2-amine | |
| Other names
2,5-Dimethoxy-4-amyl-amphetamine;
2,5-Dimethoxy-4-amyl-1-ethyl-(alpha-methyl)amine | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| Abbreviations | DOAM |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C16H27NO2 | |
| Molar mass | 265.39 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Dimethoxy-4-amylamphetamine (DOAM) is a lesser-known psychedelic drug and a substituted amphetamine. DOAM was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin. In his book PiHKAL (Phenethylamines i Have Known And Loved), the minimum dosage is listed as 10 mg, and the duration is unknown. DOAM produces a bare threshold and tenseness. As the 4-alkyl chain length is increased from shorter homologues such as DOM, DOET and DOPR which are all potent hallucinogens, the 5-HT2 binding affinity increases, rising to a maximum with the 4-(n-hexyl) derivative before falling again with even longer chains, but compounds with chain length longer than n-propyl, or with other bulky groups such as isopropyl, t-butyl or γ-phenylpropyl at the 4- position, fail to substitute for hallucinogens in animals or produce hallucinogenic effects in humans, suggesting these have low efficacy and are thus antagonists or partial agonists at the 5-HT2A receptor.[1][2][3][4]
See also
- 2,5-Dimethoxy-4-Substituted Amphetamines
References
- ↑ "Psychotomimetic phenylisopropylamines. 5. 4-Alkyl-2,5-dimethoxyphenylisopropylamines". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 18 (12): 1201–4. December 1975. doi:10.1021/jm00246a006. PMID 1195275.
- ↑ "A structure-affinity study of the binding of 4-substituted analogues of 1-(2,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-2-aminopropane at 5-HT2 serotonin receptors". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 33 (3): 1032–6. March 1990. doi:10.1021/jm00165a023. PMID 2308135.
- ↑ "1-[4-(3-Phenylalkyl)phenyl]-2-aminopropanes as 5-HT(2A) partial agonists". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 43 (16): 3074–84. August 2000. doi:10.1021/jm9906062. PMID 10956215.
- ↑ Kruegel AC. Phenalkylamines and Methods of Making and Using the Same. Patent WO 2022/192781
External links
 |

