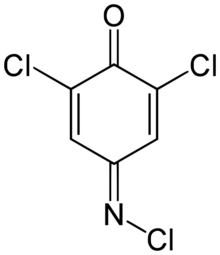
Chemistry:2,6-Dichloroquinone-4-chloroimide
From HandWiki
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2,6-Dichloro-4-(chloroimino)cyclohexa-2,5-dien-1-one | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H2Cl3NO | |
| Molar mass | 210.44 g·mol−1 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |  
|
| GHS Signal word | Warning |
| H242, H315, H319, H335 | |
| P210, P220, P234, P261, P264, P271, P280, P302+352, P304+340, P305+351+338, P312, P321, P332+313, P337+313, P362, P370+378, P403+233, P403+235, P405, P411, P420, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
2,6-Dichloroquinone-4-chloroimide (Gibbs reagent) is an organic compound used as an colorimetric indicator to detect phenolic compounds.[1] Upon reaction with phenol itself, 2,6-dichlorophenolindophenol is formed,[2] a chemical that is used as a redox indicator.
References
- ↑ Arip, Mohamad Nasir Mat; Heng, Lee Yook; Ahmad, Musa; Aishah Hasbullah, Siti (2013). "Reaction of 2,6-dichloroquinone-4-chloroimide (Gibbs reagent) with permethrin – an optical sensor for rapid detection of permethrin in treated wood". Chem Cent J 7: 122. doi:10.1186/1752-153X-7-122. PMID 23867006.
- ↑ Svobodová, D.; Křenek, P.; Fraenkl, M.; Gasparič, J. (1977). "Colour Reaction of Phenols with the Gibbs Reagent. The Reaction Mechanism and Decomposition and Stabilisation of the Reagent.". Microchim. Acta 67 (3–4): 251–264. doi:10.1007/BF01213035.
 |

