Chemistry:2-Hydroxybenzylamine
From HandWiki
Short description: Chemical compound
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C7H9NO |
| Molar mass | 123.155 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
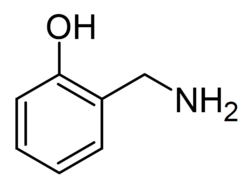
2-Hydroxybenzylamine (2-HOBA, marketed as Hobamine) is a natural product found in Himalayan tartary buckwheat (Fagopyrum tataricum). It acts as an antioxidant and scavanger of free radicals and isolevuglandins and is sold as a dietary supplement.[1][2][3][4]
References
- ↑ "In vitro safety pharmacology evaluation of 2-hydroxybenzylamine acetate". Food and Chemical Toxicology 121: 541–548. November 2018. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2018.09.047. PMID 30253245.
- ↑ "Scavenging of reactive dicarbonyls with 2-hydroxybenzylamine reduces atherosclerosis in hypercholesterolemic Ldlr-/- mice". Nature Communications 11 (1): 4084. August 2020. doi:10.1038/s41467-020-17915-w. PMID 32796843. Bibcode: 2020NatCo..11.4084T.
- ↑ "Scavenging Reactive Lipids to Prevent Oxidative Injury". Annual Review of Pharmacology and Toxicology 61: 291–308. January 2021. doi:10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-031620-035348. PMID 32997599.
- ↑ "2-Hydroxybenzylamine (2-HOBA) to prevent early recurrence of atrial fibrillation after catheter ablation: protocol for a randomized controlled trial including detection of AF using a wearable device". Trials 22 (1): 576. August 2021. doi:10.1186/s13063-021-05553-6. PMID 34454591.
 |

