Chemistry:APICA (drug)
From HandWiki
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| ChemSpider | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
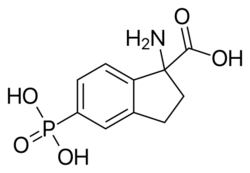
| Formula | C10H12NO5P |
| Molar mass | 257.182 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
1-Amino-5-phosphonoindan-1-carboxylic acid (APICA) is a drug that is used in neuroscience research. It is a selective antagonist for the group II metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluR2/3), and has been useful in the study of this receptor subfamily.[1][2][3][4][5]
References
- ↑ "Synthesis and biological activity of cyclic analogues of MPPG and MCPG as metabotropic glutamate receptor antagonists.". Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters 7 (9): 1195–1198. May 1997. doi:10.1016/S0960-894X(97)00177-7.
- ↑ "Asymmetric Strecker-Type Reaction of alpha-Aryl Ketones. Synthesis of (S)-alphaM4CPG, (S)-MPPG, (S)-AIDA, and (S)-APICA, the Antagonists of Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors". The Journal of Organic Chemistry 64 (1): 120–125. January 1999. doi:10.1021/jo981297a. PMID 11674092.
- ↑ "Group II metabotropic glutamate receptors modulate extracellular glutamate in the nucleus accumbens". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 300 (1): 162–71. January 2002. doi:10.1124/jpet.300.1.162. PMID 11752112.
- ↑ "The origin and neuronal function of in vivo nonsynaptic glutamate". The Journal of Neuroscience 22 (20): 9134–41. October 2002. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-20-09134.2002. PMID 12388621.
- ↑ "Activation of Group II/III metabotropic glutamate receptors attenuates LPS-induced astroglial neurotoxicity via promoting glutamate uptake". Journal of Neuroscience Research 84 (2): 268–77. August 2006. doi:10.1002/jnr.20897. PMID 16752416.

