Chemistry:Amphomycin
From HandWiki
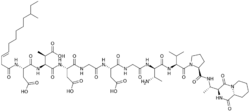
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C58H91N13O20 | |
| Molar mass | 1290.437 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
Amphomycin is an antibiotic with the molecular formula C58H91N13O20 which is produced by the bacterium Streptomyces canus.[1][2][3]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 "Amphomycin" (in en). Pubchem.ncbi.NLM.nih.gov. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Amphomycin#section=IUPAC-Name.
- ↑ HEINEMANN, B; KAPLAN, MA; MUIR, RD; HOOPER, IR (December 1953). "Amphomycin, a new antibiotic.". Antibiotics & Chemotherapy (Northfield, Ill.) 3 (12): 1239–42. PMID 24542804.
- ↑ Korzybski, Tadeusz; Kowszyk-Gindifer, Zuzanna; Kurylowicz, Wlodzimierz (3 September 2013) (in en). Antibiotics: Origin, Nature and Properties. Elsevier. p. 399. ISBN 978-1-4832-2305-6.
Further reading
- Marshall, J. (2 December 2012) (in en). Mechanisms of Saccharide Polymerization and Depolymerization. Elsevier. pp. 14. ISBN 978-0-323-14969-3.
- (in en) Cell Surface and Extracellular Glycoconjugates: Structure and Function. Academic Press. 2 December 2012. p. 141. ISBN 978-0-323-13809-3.
- (in en) Advances in Carbohydrate Chemistry and Biochemistry. Academic Press. 27 January 1983. p. 342. ISBN 978-0-08-056299-5.
- Bodanszky, Miklos.; Sigler, Gerald F.; Bodanszky, Agnes. (April 1973). "Structure of the peptide antibiotic amphomycin". Journal of the American Chemical Society 95 (7): 2352–2357. doi:10.1021/ja00788a040. PMID 4709239.
 |
