Chemistry:Aniline Blue WS
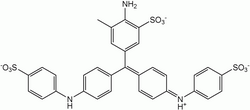
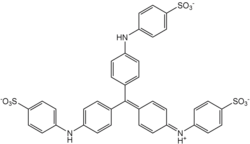
Aniline Blue WS, also called aniline blue, diphenylamine blue, China blue, or Soluble blue, is a mixture of methyl blue and water blue. It may also be either one of them.[1] It is a soluble dye used as a biological dye,[2] in fluorescence microscopy, appearing a yellow-green colour after excitation with violet light.[3] It is a mixture of the trisulfonates of triphenyl rosaniline and of diphenyl rosaniline.[4]
Aniline blue or its constituents are used to stain collagen, as the fibre stain in Masson's trichrome,[5] as well as to reveal callose structures in plant tissues.[6]
It can also be used in other connective tissue stains, such as Mallory's stain,[5] Gömöri trichrome stain, and Carstair's Method.[7] It is used in differential staining.
References
- ↑ "Stainsfile - Aniline blue WS". http://stainsfile.info/StainsFile/dyes/707.htm.
- ↑ "Medical Definition of ANILINE BLUE". http://www.merriam-webster.com/medical/aniline+blue.
- ↑ "Fluorescence Microscope Images". http://www.biologie.uni-hamburg.de/b-online/library/webb/BOT410/410Labs/Fluor-99/fluorescence_microscope_images.htm.
- ↑ "aniline blue". http://medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/aniline+blue.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 "Stainsfile - Water blue". http://stainsfile.info/StainsFile/dyes/42755.htm.
- ↑ "Protocols - Staining with trypan blue and aniline blue - Felix Mauch's Group". http://commonweb.unifr.ch/biol/pub/mauchgroup/staining.html.
- ↑ Carstairs, K. C. (1965). "The Identification of platelets and platelet antigens in histological sections". The Journal of Pathology and Bacteriology 90 (1): 225-231.
 |
