Chemistry:Aspartame-acesulfame salt
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
[2-carboxyl-1-(N-(1-methoxycarbonyl-2-phenyl)ethylcarbamoyl)]ethanaminium 6-methyl-4-oxo-1,2,3-oxathiazin-3-ide-2,2-dioxide
| |
| Other names
Salt of Aspartame-acesulfame
Twinsweet
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
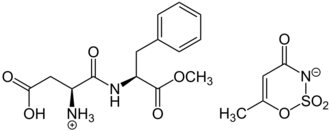
| C18H23N3O9S | |
| Molar mass | 457.45 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | white crystalline powder |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Aspartame-acesulfame salt is an artificial sweetener marketed under the name Twinsweet. It is produced by soaking a 2:1 mixture of aspartame and acesulfame potassium in an acidic solution and allowing it to crystallize; moisture and potassium are removed during this process. It is approximately 350 times as sweet as sucrose. It has been given the E number E962.[2]
History
Aspartame-acesulfame salt was invented in 1995 by sweetener expert Dr John Fry[3] while working for The Holland Sweetener Company (HSC), a subsidiary of DSM. HSC marketed it with the name Twinsweet. It was approved for use as an artificial sweetener in the European Parliament and Council Directive 94/35 EC as amended by Directive 2003/115/EC in 2003. In North America, it falls under the same regulations as aspartame and acesulfame-K. It is also approved for use in China, Russia, Hong Kong, Australia, and New Zealand.
In December 2006, HSC ceased all of its aspartame operations, citing a glut in the market driving prices below profitable values.[4] The rights to aspartame-acesulfame are now owned by The NutraSweet Company Inc., who has continued to market the sweetener successfully in the United States and European Union.
References
- ↑ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2008-09-10. https://web.archive.org/web/20080910124100/http://www.food.gov.uk/multimedia/pdfs/Dossier_aspartame.pdf. Retrieved 2007-10-21.
- ↑ "Holland Sweetener rolls out Twinsweet". BakeryAndSnacks.com (William Reed Business Media). November 19, 2003. http://www.bakeryandsnacks.com/Processing-Packaging/Holland-Sweetener-rolls-out-Twinsweet. Retrieved July 29, 2011.
- ↑ US Patent 5827562, Sweetener Salts
- ↑ "DSM pulls out of aspartame market". FoodNavigator. 2006-03-30. http://www.foodnavigator-usa.com/news-by-product/news.asp?id=66736.[yes|permanent dead link|dead link}}]
External links
 |
