Chemistry:Aviculin
From HandWiki
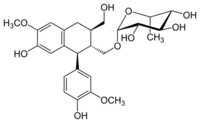
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
[(1S,2R,3R)-7-Hydroxy-1-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-3-(hydroxymethyl)-6-methoxy-1,2,3,4-tetrahydronaphthalen-2-yl]methyl α-L-rhamnopyranoside
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(2R,3R,4R,5R,6S)-2-{[(1S,2R,3R)-7-Hydroxy-1-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-3-(hydroxymethyl)-6-methoxy-1,2,3,4-tetrahydronaphthalen-2-yl]methoxy}-6-methyloxane-3,4,5-triol | |
| Other names
isolariciresinol-9'-rhamnopyranoside
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C26H34O10 | |
| Molar mass | 506.54 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
Aviculin is a lignan. It is bio-active isolate of Pseudocydonia sinensis [2] or Polygonum aviculare.[3]
References
- ↑ "KNApSAcK Metabolite Information - C00031615". http://www.knapsackfamily.com/knapsack_core/information.php?word=C00031615.
- ↑ "Antitumor-promoting constituents from Chaenomeles sinensis KOEHNE and their activities in JB6 mouse epidermal cells". Chem. Pharm. Bull. 51 (11): 1318–21. November 2003. doi:10.1248/cpb.51.1318. PMID 14600382.
- ↑ Ja Kim, Hyoung (1994). "A Novel Lignan and Flavonoids from Polygonum aviculare". Journal of Natural Products 57 (5): 581–586. doi:10.1021/np50107a003.
 |
