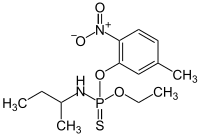
Chemistry:Butamifos
| |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C13H21N2O4PS | |
| Molar mass | 332.35 g·mol−1 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |  
|
| GHS Signal word | Warning |
| H302, H410 | |
| P264, P270, P273, P301+317Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, P330, P391, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Butamifos is an herbicide that is used to control weeds.[2]
Production
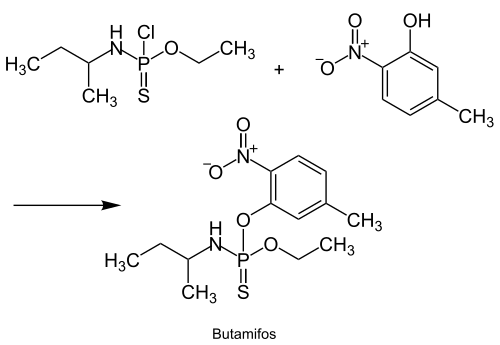
The production of butamifos is based on N-[chloro(ethoxy)phosphinothioyl]butan-2-amine and 5-methyl-2-nitrophenol and is described in the following reaction sequence:[3]
Properties
Butamifos is a chiral molecule. The technical product uses a mixture of the (R)- and (S)-isomers.[4]
In a study, the level of pesticide contamination in soil and water of an agriculturally intensive area in Nepal was investigated. Endosulfan, Iprobefos, monocrotophos, mevinphos, and butamifos were detected in water samples, while cypermethrin, dichlorvos, and cyfluthrin were detected in soil samples. The increased concentration of butamifos in water may be due to higher water solubility and lower affinity for adsorption in soil.[5]
Use
Application and mode of action
Butamifos is used on beans, turf and various vegetables.[3] The active ingredient is a non-systemic, selective herbicide. Its effect is based on inhibition of microtubule formation. It also acts as an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor, making it moderately toxic to mammals.[4][6]
Trade name
A crop protection product containing the active ingredient butamifos is marketed under the trade name Cremart.[3]
Registration
No plant protection products containing butamifos are registered in the European Union or Switzerland.[7]
References
- ↑ "Butamifos" (in en). https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/37419#section=Safety-and-Hazards.
- ↑ Toshiyuki Katagi (March 1993), "Photochemistry of organophosphorus herbicide butamifos" (in German), Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 41 (3): pp. 496–501, doi:10.1021/jf00027a028, ISSN 0021-8561
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Thomas A. Unger (1996), [[1], p. 376, at Google Books "Butamifos"] (in German), Pesticide Synthesis Handbook (Elsevier): p. 376, doi:10.1016/b978-081551401-5.50299-9, ISBN 978-0-8155-1401-5, [2], p. 376, at Google Books
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Butamifos in the Pesticide Properties DataBase (PPDB)
- ↑ Kafle, B. K., Pokhrel, B., Shrestha, S., Raut, R., Dahal, B. M. (2015), "Determination of pesticide residues in water and soil samples from Ansikhola watershed, Kavre, Nepal" (in German), International Journal of Geology, Earth & Environmental Sciences 5 (2): pp. 119-127, https://www.researchgate.net/publication/281430111
- ↑ Paranjape, Kalyani. (2014) (in German), [[3], p. 74, at Google Books The pesticide encyclopedia], Wallingford, Oxfordshire UK: CABI, p. 74, ISBN 978-1-78064-014-3, [4], p. 74, at Google Books
- ↑ "European Commission Directorate-General for Health and Food Safety". https://ec.europa.eu/food/plant/pesticides/eu-pesticides-database/active-substances/?event=as.details&as_id=682.
 |
