Chemistry:Cannflavin
From HandWiki
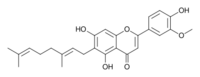 Cannflavin A
| |
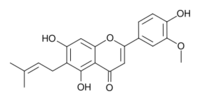 Cannflavin B
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC names
6-[(2E)-3,7-Dimethylocta-2,6-dienyl]-5,7-dihydroxy-2-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)chromen-4-one (A)
5,7-Dihydroxy-2-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-6-(3-methylbut-2-enyl)chromen-4-one (B) | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| Properties | |
| C26H28O6 (A) C21H20O6 (B) | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
Cannflavins are a group of chemical compounds found in Cannabis sativa.[1] Chemically, they are prenylflavonoids and are unrelated to THC and other cannabinoids. Cannflavins A and B were first identified in the 1980s and cannflavin C was identified in 2008.[2]
Because cannflavins A and B are inhibitors of prostaglandin E2 production in vitro,[1][3] the cannflavins have been studied for their potential use as anti-inflammatory agents.[4]
Biosynthesis
Cannflavins A and B are biosynthesized by prenylation of chrysoeriol.[5]

References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Barrett, M. L.; Scutt, A. M.; Evans, F. J. (1986). "Cannflavin A and B, prenylated flavones from Cannabis sativa L". Experientia 42 (4): 452–453. doi:10.1007/BF02118655. PMID 3754224.
- ↑ Radwan, Mohamed M.; Elsohly, Mahmoud A.; Slade, Desmond; Ahmed, Safwat A.; Wilson, Lisa; El-Alfy, Abir T.; Khan, Ikhlas A.; Ross, Samir A. (2008). "Non-cannabinoid constituents from a high potency Cannabis sativa variety". Phytochemistry 69 (14): 2627–2633. doi:10.1016/j.phytochem.2008.07.010. PMID 18774146.
- ↑ Barrett, M.L.; Gordon, D.; Evans, F.J. (1985). "Isolation from cannabis sativa L. Of cannflavin—a novel inhibitor of prostaglandin production". Biochemical Pharmacology 34 (11): 2019–2024. doi:10.1016/0006-2952(85)90325-9. PMID 3859295.
- ↑ , Wikidata Q114911513
- ↑ , Wikidata Q92444776
- ↑ , Wikidata Q92444776
 |
