Chemistry:Chaetochromin
From HandWiki
Short description: Chemical compound
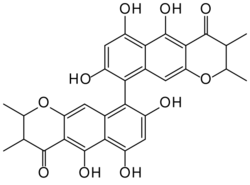 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | 4548-G05 |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C30H26O10 |
| Molar mass | 546.528 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Chaetochromin, also known as 4548-G05, is an orally active, small-molecule, selective agonist of the insulin receptor.[1] It has potent and long-lasting antidiabetic activity in vivo in mice.[1] The drug may represent a novel potential therapeutic agent for the treatment of diabetes which is more convenient and tolerable to administer than injected insulin.[1] It was discovered in 1981 in Chaetomium gracile fungi,[2] and its interaction with the insulin receptor was identified in 2014.[1]
Stereochemistry
Chaetochromin A and B are stereoisomers of this structure, while chaetochromin C and D are related but different compounds.[3] It is not known whether the insulin mimetic effect was found in chaetochromin A or B, or in a mixture.[1]
See also
- Anti-diabetic medication
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 "Identification of a small molecular insulin receptor agonist with potent antidiabetes activity". Diabetes 63 (4): 1394–1409. April 2014. doi:10.2337/db13-0334. PMID 24651808.
- ↑ "Mycotoxin production by Chaetomium spp. and related fungi". Canadian Journal of Microbiology 27 (8): 766–772. August 1981. doi:10.1139/m81-119. PMID 7296410.
- ↑ "Chaetochromin". PubChem. U.S. National Library of Medicine. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pccompound?term=chaetochromin.
 |

