Chemistry:Chamigrene
From HandWiki
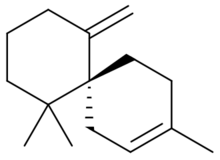
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(R)-11-Methylene-3,7,7-trimethylspiro[5.5]undec-2-ene[1]
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C15H24 | |
| Molar mass | 204.357 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
(−)-β-Chamigrene is the parent compound of subclass of sesquiterpenes found in various marine and terrestrial plants. The stereoisomer (−)-β-chamigrene is the most common in nature.[citation needed]
Chamigrenes (chamigrene-related compounds) are characterized by a spiro[5.5]undecane core with an all-carbon quaternary stereocenter at the junction of the spirocycle.[2]
References
- ↑ Template:Aldrich
- ↑ David E. White, Ian C. Stewart, Brinton A. Seashore-Ludlow, Robert H. Grubbs, and Brian M.Stoltz (2010). "A general enantioselective route to the chamigrene natural product family". Tetrahedron 66 (26): 4668–4686. doi:10.1016/j.tet.2010.04.128. PMID 20798895.
 |

