Chemistry:Chiral phosphoric acid
From HandWiki
Short description: Esters of phosphoric acid with a chiral backbone
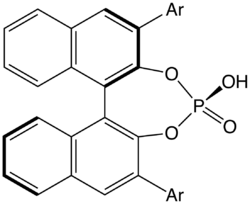
Structure of a common class of BINOL-derived chiral phosphoric acids. Catalysts of this type are also known as Akiyama–Terada catalysts (after Takahiko Akiyama and Masahiro Terada). Common examples of Ar include Ar = 4-NO
2-C
6H
4, 9-anthracenyl, and 2, 4, 6-iPr
3-C
6H
2 (commonly known as TRIP[1]).
2-C
6H
4, 9-anthracenyl, and 2, 4, 6-iPr
3-C
6H
2 (commonly known as TRIP[1]).
In organic chemistry, chiral phosphoric acids are esters of phosphoric acid H
3PO
4 that have chiral backbones. Well known examples include cyclic diesters derived from the BINOL and TADDOL motifs. These compounds are used in asymmetric catalysis as chiral Brønsted acids and/or hydrogen-bond donors.[2] The conjugate bases are also used in generating chiral ion pairs.[3]
References
- ↑ Klussmann, Martin; Ratjen, Lars; Hoffmann, Sebastian; Wakchaure, Vijay; Goddard, Richard; List, Benjamin (September 2010). "Synthesis of TRIP and Analysis of Phosphate Salt Impurities" (in en). Synlett 2010 (14): 2189–2192. doi:10.1055/s-0030-1258505. ISSN 0936-5214. http://www.thieme-connect.de/DOI/DOI?10.1055/s-0030-1258505.
- ↑ "Chiral Phosphoric Acids". https://www.strem.com/uploads/resources/documents/chiral_phos_acids.pdf.
- ↑ Parmar, Dixit; Sugiono, Erli; Raja, Sadiya; Rueping, Magnus (2014). "Complete Field Guide to Asymmetric BINOL-Phosphate Derived Brønsted Acid and Metal Catalysis: History and Classification by Mode of Activation; Brønsted Acidity, Hydrogen Bonding, Ion Pairing, and Metal Phosphates". Chemical Reviews 114 (18): 9047–9153. doi:10.1021/cr5001496. PMID 25203602.
 |

