Chemistry:Cryptolepine
From HandWiki
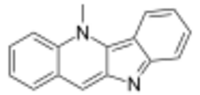
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
5-Methyl-5H-indolo[3,2-b]quinoline | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C16H12N2 | |
| Molar mass | 232.286 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
Cryptolepine is an alkaloid with antimalarial and cytotoxic properties, in vitro and in mice. It is able to intercalate into DNA at the cytosine-cytosine sites.[1][2] Because of its toxicity, Cryptolepine is not considered appropriate for use as an anti-malarial drug in humans.[3]
Cryptolepine can be found in the roots of the West African plant, Cryptolepis sanguinolenta.[1]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Wright, C. W.; Addae-Kyereme, J.; Breen, A. G.; Brown, J. E.; Cox, M. F.; Croft, S. L.; Gökçek, Y.; Kendrick, H. et al. (2001). "Synthesis and evaluation of cryptolepine analogues for their potential as new antimalarial agents". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 44 (19): 3187–3194. doi:10.1021/jm010929+. PMID 11543688.
- ↑ Onyeibor, O.; Croft, S. L.; Dodson, H. I.; Feiz-Haddad, M.; Kendrick, H.; Millington, N. J.; Parapini, S.; Phillips, R. M. et al. (2005). "Synthesis of Some Cryptolepine Analogues, Assessment of Their Antimalarial and Cytotoxic Activities, and Consideration of Their Antimalarial Mode of Action". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 48 (7): 2701–2709. doi:10.1021/jm040893w. PMID 15801861.
- ↑ Gopalan, Rajendran C.; Emerce, Esra; Wright, Colin W.; Karahalil, Bensu; Karakaya, Ali E.; Anderson, Diana (December 2011). "Effects of the anti-malarial compound cryptolepine and its analogues in human lymphocytes and sperm in the Comet assay". Toxicology Letters 207 (3): 322–325. doi:10.1016/j.toxlet.2011.09.010. PMID 21946165.
 |
