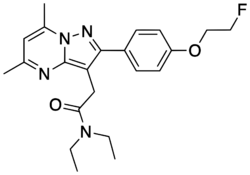
Chemistry:DPA-714
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| |
| CAS Number | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C22H27FN4O2 |
| Molar mass | 398.482 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
DPA-714 or N,N-diethyl-2-[4-(2-fluoroethoxy)phenyl]-5,7-dimethylpyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine-3-acetamide is a selective ligand for the translocator protein (TSPO) currently under evaluation for several clinical applications.[1] For this reason, a practical, multigram synthetic route for its preparation has been described.[2]
The binding affinity of DPA-714 for TSPO is reported as Ki = 7.0 ± 0.4 nM.[3][4]
[18F]DPA-714 is currently under investigation as a potential radiopharmaceutical for imaging TSPO in living systems using positron emission tomography (PET). DPA-714, along with other members of the DPA class of TSPO ligands, has been shown to decrease microglial activation and increase neuronal survival in a quinolinic acid rat model of excitotoxic neurodegeneration, suggesting potential neuroprotective effects.[5]
See also
References
- ↑ "Pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine acetamides: 4-Phenyl alkyl ether derivatives as potent ligands for the 18 kDa translocator protein (TSPO)". Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters 20 (19): 5799–5802. October 2010. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2010.07.135. PMID 20727749.
- ↑ "A practical, multigram synthesis of the 2-(2-(4-alkoxyphenyl)-5,7-dimethylpyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-3-yl)acetamide (DPA) class of high affinity translocator protein (TSPO) ligands". Tetrahedron Letters 53 (29): 3780–3783. 2012. doi:10.1016/j.tetlet.2012.05.044.
- ↑ "DPA-714, a new translocator protein-specific ligand: synthesis, radiofluorination, and pharmacologic characterization". Journal of Nuclear Medicine 49 (5): 814–822. May 2008. doi:10.2967/jnumed.107.046151. PMID 18413395.
- ↑ "Radiosynthesis of [18F]DPA-714, a selective radioligand for imaging the translocator protein (18 kDa) with PET". Journal of Labelled Compounds and Radiopharmaceuticals 51 (7): 286–292. 2008. doi:10.1002/jlcr.1523.
- ↑ "Effects of translocator protein (18 kDa) ligands on microglial activation and neuronal death in the quinolinic-acid-injected rat striatum". ACS Chemical Neuroscience 3 (2): 114–119. February 2012. doi:10.1021/cn200099e. PMID 22860181.
 |

