Chemistry:Dithionous acid
From HandWiki
|
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Dithionous acid
| |||
| Other names
Hydrosulfurous acid; Hyposulfurous acid
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| H2S2O4 | |||
| Molar mass | 130.144 g/mol | ||
| Acidity (pKa) | 0.35, 2.45 [1] | ||
| Conjugate base | Dithionite | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Related compounds
|
Oxalic acid Sodium dithionite Potassium dithionite | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
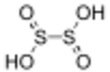
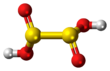
Dithionous acid is a sulfur oxoacid with the chemical formula H2S2O4. It is unstable in pure form,[2] but its salts, known as dithionites, are stable.
It was initially assumed that the C2 symmetric structure HOS(=O)-S(=O)OH is the most stable among molecules with the formula H2S2O4 using ab initio calculations.[2] The reason for this is the existence of intermolecular hydrogen bonds. It is now known that dithionous acid spontaneously decomposes to SO2 and S(OH)2.
Sodium dithionite is a white powder used as a reductant and a bleaching agent. It is also used to reduce the nitro group to an amino group in organic reactions.
References
- ↑ Catherine E. Housecroft; Alan G. Sharpe (2008). "Chapter 16: The group 16 elements". Inorganic Chemistry, 3rd Edition. Pearson. p. 520. ISBN 978-0-13-175553-6.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Drozdova, Yana; Steudel, Ralf; Hertwig, Roland H.; Koch, Wolfram; Steiger, Thomas (1998). "Structures and Energies of Various Isomers of Dithionous Acid, H2S2O4, and of Its Anion HS2O4- 1". The Journal of Physical Chemistry A 102 (6): 990–996. doi:10.1021/jp972658d. Bibcode: 1998JPCA..102..990D.
 |