Chemistry:Ethyl macadamiate
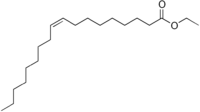 Ethyl oleate, a major constituent of ethyl macadamiate
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Floramac 10
| |
| Identifiers | |
| DrugBank | |
| Properties | |
| Appearance | Clear, colorless liquid |
| Density | 0.88 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 10 °C (50 °F; 283 K) (congeals) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Ethyl macadamiate is the ester of ethyl alcohol and the fatty acids derived from Macadamia ternifolia seed oil.[1] Ethyl macadamiate is used in some cosmetic formulations.[1]
Chemical structure
Ethyl macadamiate is a mixture of the ethyl esters of the free fatty acids produced by the complete saponification of macadamia oil. The primary constituents of ethyl macadamiate are ethyl oleate and ethyl palmitoleate.
Physical properties
Ethyl macadamiate is a clear, colorless liquid at room temperature, with a typical fatty ester odor. Ethyl macadamiate's melting (congealing) point is 10 °C (50 °F) and its specific gravity is 0.88. Ethyl macadamiate spreads very aggressively, and has a light, nongreasy dry skinfeel similar to that of some silicone derivatives, however, ethyl macadamiate is non-volatile.
Uses
Ethyl macadamiate is used in cosmetics, especially in skincare, haircare and suncare formulation. The dry skinfeel and high spread make ethyl macadamiate well suited for increasing sunscreen coverage. Ethyl macadamiate is an alternative to cyclomethicone and dimethicone as a skinfeel modifier where a botanical, nonvolatile and/or lipid-soluble substance is preferred.
References
 |

