Chemistry:Faustite
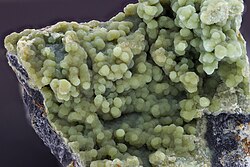
The IMA-approved mineral faustite[1] is a member of the triclinic turquoise group of hydrous phosphates with the chemical composition
ZnAl
6(PO
4)
4(OH)
8 · 4H2O. It is named after the American mineralogist and petrologist Dr. George Tobias Faust, who workes with the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS).[2]
Some divalent copper generally replaces the zinc position. Faustite is the zinc-rich analogue of turquoise, having almost four times as much zinc than copper in its crystal structure.[3] Trivalent (ferric) iron may replace some of the aluminum. Minor amounts of calcium may also be present. It has a hardness of 4.5–5.5 on the Mohs scale of mineral hardness, and aside from having a slightly lower hardness, it may be difficult to distinguish it from turquoise in hand specimens.
Faustite has a blue-green to apple green color in polished cabochons. It may be presented as a turquoise imitation and also be treated with stabilizers for jewelry making.
References
- ↑ "Faustite". RRUFF Project. Mineral Data Publishing. https://rruff.info/doclib/hom/faustite.pdf.
- ↑ Faustite, MinDat.org, http://www.mindat.org/show.php?id=1623
- ↑ Faustite Mineral Data, WebMineral.com, https://webmineral.com/data/Faustite.shtml#.U0M57KLDu2A
- IMA Database of Mineral Properties - Faustite
- Mindat.org - Faustite
- Webmineral.com - Faustite Mineral Data
 |
