Chemistry:Galvinoxyl
From HandWiki
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
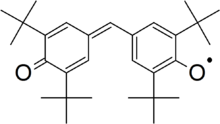
| Preferred IUPAC name
4-[(3,5-Di-tert-butyl-4-oxocyclohexa-2,5-dien-1-ylidene)methyl]-2,6-di-tert-butylphenoxyl | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C29H41O2 | |
| Molar mass | 421.645 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Galvinoxyl is a commercially available radical scavenger.[1] It finds use both as a probe for studying radical reactions and as an inhibitor of radical polymerization. It may be synthesized by oxidation of the parent phenol with lead dioxide or potassium hexacyanoferrate(III). Its radical structure is confirmed by the loss of the O–H stretch in the IR spectrum and by electron spin resonance; it is stable even in the presence of oxygen.[2][3]
References
- ↑ RajanBabu, T. V. (2001). "Galvinoxyl". Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis. doi:10.1002/047084289X.rg001.
- ↑ Coppinger, Galvin M. (1957). "A Stable Phenoxy Radical Inert to Oxygen". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 79 (2): 501. doi:10.1021/ja01559a073.
- ↑ Kharasch, M. S.; Joshi, B. S. (1957). "Reactions of Hindered Phenols. II. Base-Catalyzed Oxidations of Hindered Phenols". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 22 (11): 1439. doi:10.1021/jo01362a034.
 |

