Chemistry:Gregatin B
From HandWiki
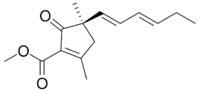
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Methyl (5R)-5-[(1E,3E)-hexa-1,3-dienyl]-2,5-dimethyl-4-oxofuran-3-carboxylate[1]
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C14H18O4 | |
| Molar mass | 250.294 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
Gregatin B is a metabolite of the fungi Cephalosporium gregatum and Aspergillus panamensis with the molecular formula C14H18O4[2][3] Gregatin B is a weak antibiotic.[4][3] Gregatin B was discovered in 1982[3] and has been the subject of total synthesis.[5][6]
References
- ↑ "Gregatin B" (in en). Pubchem.ncbi.NLM.nih.gov. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Gregatin-B#section=3D-Conformer.
- ↑ Durbin, R. (2 December 2012) (in en). Toxins in Plant Disease. Elsevier. p. 410. ISBN 978-0-323-14704-0.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Buckingham, John (1987) (in en). Dictionary of Organic Compounds. Taylor & Francis. p. 367. ISBN 978-0-412-17050-8.
- ↑ Bycroft, Barrie W.; Payne, David J. (9 August 2013) (in en). Dictionary of Antibiotics and Related Substances: with CD-ROM, Second Edition. CRC Press. p. 892. ISBN 978-1-4822-8215-3.
- ↑ "Gregatin B | Chemical Substance Information | J-GLOBAL" (in en). Jglobal.JST.go.jp. https://jglobal.jst.go.jp/en/detail?JGLOBAL_ID=201307045889172378.
- ↑ Kusakabe, Taichi; Kawai, Yasuko; Kato, Keisuke (4 October 2013). "Total Synthesis of (+)-Gregatin B and E". Organic Letters 15 (19): 5102–5105. doi:10.1021/ol402472q. PMID 24066736.
Further reading
- Wijeratne, E. M. Kithsiri; Xu, Yaming; Arnold, A. Elizabeth; Gunatilaka, A. A. Leslie (January 2015). "Pulvinulin A, Graminin C, and cis-Gregatin B – New Natural Furanones from Pulvinula sp. 11120, a Fungal Endophyte of Cupressus arizonica". Natural Product Communications 10 (1): 1934578X1501000. doi:10.1177/1934578x1501000127. ISSN 1934-578X.
- Burghart-Stoll, H; Brückner, R (20 May 2011). "A serendipitous synthesis of (+)-gregatin B, second structure revisions of the aspertetronins, gregatins, and graminin A, structure revision of the penicilliols.". Organic Letters 13 (10): 2730–3. doi:10.1021/ol2008318. PMID 21526752.
- Peberdy, John F. (11 November 2013) (in en). Penicillium and Acremonium. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 222. ISBN 978-1-4899-1986-1.
 |

