Chemistry:Hydrazinium nitroformate
From HandWiki
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Hydrazine nitroform; HNF
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
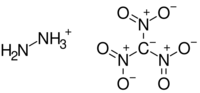
| CH5N5O6 | |
| Molar mass | 183.080 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
Hydrazinium nitroformate (HNF) is a salt of hydrazine and nitroform (trinitromethane).[1][2] It has the molecular formula [H2NNH3]+[C(NO2)3]−[3] and is soluble in most solvents.
Hydrazinium nitroformate is an energetic oxidizer. Research is being conducted at the European Space Agency to investigate its use in solid rocket propellants.[4][5] It tends to produce propellants which burn very rapidly and with very high combustion efficiency. Its high energy leads to high specific impulse propellants. It is currently an expensive research chemical available only in limited quantities. A disadvantage of HNF is its limited thermal stability.
References
- ↑ H. F. R. Schoyer, W. H. M. Welland-Veltman, J. Louwers, P. A. O. G. Korting, A. E. D. M. van der Heijden, H. L. J. Keizers, and R. P. van den Berg (2002). "Overview of the Development of Hydrazinium Nitroformate". Journal of Propulsion and Power 18 (1): 131–137. doi:10.2514/2.5908.
- ↑ P. S. Dendage, D. B. Sarwade, S. N. Asthana & H. Singh (2001). "Hydrazinium nitroformate (HNF) and HNF based propellants: A review". Journal of Energetic Materials 19 (1): 41–78. doi:10.1080/07370650108219392. Bibcode: 2001JEnM...19...41D.
- ↑ Dickens, Brian (1967). "Crystal structure of hydrazine nitroform [N2H5+C(NO2)3−]". Chemical Communications (5): 246–247. doi:10.1039/c19670000246.
- ↑ Preparing for the Future. 6. European Space Agency. March 1996.
- ↑ Tydon, Walter (31 July 1970). Minimum Cost Design Launch Vehicle Design/Costing Study TOR-0059(6526-01)2. 2, Background Studies. The Aerospace Corporation. pp. 4-13, 4-14.
 |

