Chemistry:Inosine triphosphate
From HandWiki
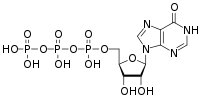
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Inosine 5′-(tetrahydrogen triphosphate)
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
O1-{[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-3,4-Dihydroxy-5-(6-oxo-1,6-dihydro-9H-purin-9-yl)oxolan-2-yl]methyl} tetrahydrogen triphosphate | |
| Other names
iniosine triphosphate
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H15N4O14P3 | |
| Molar mass | 508.165 g·mol−1 |
| 903.5 mg/mL | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
Inosine triphosphate (ITP) is an intermediate in the purine metabolism pathway, seen in the synthesis of ATP and GTP. It comprises an inosine nucleotide containing three phosphate groups esterified to the sugar moiety.
ITP results from deamination of ATP. Incorporation of ITP into the DNA from the nucleotide pool can lead to DNA damage, mutagenesis and other harmful effects.[1] ITP is processed by the enzyme inosine triphosphate pyrophosphatase (ITPA), which turns it into inosine monophosphate (IMP), to avoid incorporation into DNA.[1]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Measuring deaminated nucleotide surveillance enzyme ITPA activity with an ATP-releasing nucleotide chimera". Nucleic Acids Research 45 (20): 11515–11524. November 2017. doi:10.1093/nar/gkx774. PMID 29036687.
 |
