Chemistry:Iridomyrmecin
From HandWiki
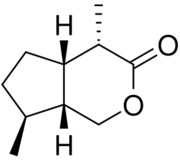
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
(4S,4aS,7S,7aR)-4,7-Dimethylhexahydrocyclopenta[c]pyran-3(1H)-one | |
| Other names
Iridomyrmexin
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H16O2 | |
| Molar mass | 168.236 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
Iridomyrmecin is a defensive chemical, classified as an iridoid, isolated from ants of the genus Iridomyrmex.[1] It has also evolved into a sex pheromone in wasps such as Leptopilina,[2] with host species using the smell of iridomyrmecin as a way of detecting the presence of the parasitoid wasps.[3] Iridomyrmecin is also found in a variety of plants including Actinidia polygama.[4]
See also
- Cat pheromone#Cat attractants for other chemicals that have behavioural effects on cats
References
- ↑ "The chemistry of ants. I. Terpenoid constituents of some Australian Iridomyrmex species". Australian Journal of Chemistry 9 (2): 288–293. 1956. doi:10.1071/CH9560288.
- ↑ "A nonspecific defensive compound evolves into a competition avoidance cue and a female sex pheromone". Nature Communications 4 (1): 2767. 2013-11-15. doi:10.1038/ncomms3767. PMID 24231727. Bibcode: 2013NatCo...4.2767W.
- ↑ "Drosophila Avoids Parasitoids by Sensing Their Semiochemicals via a Dedicated Olfactory Circuit". PLOS Biology 13 (12): e1002318. December 2015. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.1002318. PMID 26674493.
- ↑ "Exact nature of matatabilactone and the terpenes of Nepeta cataria". Tetrahedron Letters 6 (46): 4097–4102. 1965. doi:10.1016/s0040-4039(01)99572-3.
 |
