Chemistry:Jasminaldehyde
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(2Z)-2-benzylideneheptanal
| |
| Other names
alpha-Amyl cinnamaldehyde; alpha-Pentylcinnamaldehyde; Jasmonal
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |  
|
| GHS Signal word | Warning |
| H317, H411 | |
| P261, P272, P273, P280, P302+352, P321, P333+313, P363, P391, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
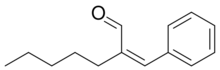
Jasminaldehyde (also known as jasmine aldehyde and α-pentylcinnamaldehyde) is a fine chemical used as an aroma compound in perfumes. It is responsible for jasmine's characteristic scent.
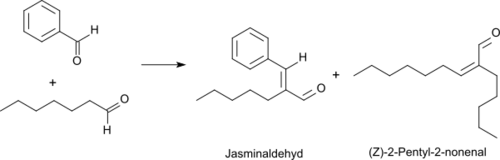
Synthesis
Jasminaldehyde used in industry is commonly derived not from jasmine essential oil, but ultimately from the castor bean plant. The process starts with ricinoleic acid, the principal constituent of castor oil. This compound undergoes cracking to undecylenic acid (used mainly to produce Nylon 11) and heptanal. The heptanal, once distilled, is then reacted with benzaldehyde in the presence of a basic catalyst (trans-aldol condensation) to give jasminaldehyde and water. The foul-smelling 2-pentylnon-2-enal is an unwanted byproduct that results from the self-condensation of heptanal.[1][2] This process parallels the preparation hexyl cinnamaldehyde from octanal and benzaldehyde.
References
- ↑ Heynderickx, Philippe M. (2019-08-05). "Activity Coefficients for Liquid Organic Reactions: Towards a Better Understanding of True Kinetics with the Synthesis of Jasmin Aldehyde as Showcase" (in en). International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20 (15): 3819. doi:10.3390/ijms20153819. ISSN 1422-0067. PMID 31387255.
- ↑ G. A. Burdock, Fenaroli’s Handbook of Flavor Ingredients, Fifth Edition, 2005, CRC Press, Boca Raton, Fl., ISBN 0-8493-3034-3
 |