Chemistry:Limonin
From HandWiki
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
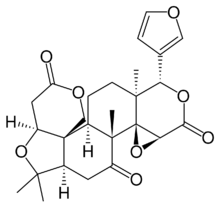
(2aR,4aR,4bR,5aS,8S,8aS,10aR,10bR,14aS)-8-(Furan-3-yl)-2,2,4a,8a-tetramethyldecahydro-11H,13H-oxireno[2,3-c]pyrano[4′′,3′′:2′,3′]furo[3′,4′:5,6]naphtho[1,2-d]pyran-4,6,13(2H,5aH)-trione | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C26H30O8 | |
| Molar mass | 470.52 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
Limonin is a limonoid, and a bitter, white, crystalline substance found in citrus and other plants. It is also known as limonoate D-ring-lactone and limonoic acid di-delta-lactone. Chemically, it is a member of the class of compounds known as furanolactones.
Sources
Limonin is enriched in citrus fruits and is often found at higher concentrations in seeds, for example orange and lemon seeds.[1]
Presence in citrus products
Limonin and other limonoid compounds contribute to the bitter taste of some citrus food products. Researchers have proposed removal of limonoids from orange juice and other products (known as "debittering") through the use of polymeric films.[2]
Research
Limonin is under basic research to assess its possible biological properties.[1]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Limonin". PubChem, US National Library of Medicine. 17 December 2022. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Limonin.
- ↑ Fayoux, S. P. C.; Hernandez, R. J.; Holland, R. V. (2007). "The Debittering of Navel Orange Juice Using Polymeric Films". Journal of Food Science 72 (4): E143–E154. doi:10.1111/j.1750-3841.2007.00283.x. PMID 17995766.
External links
- "Citrus Compound: ready to help your body!" (Agricultural Research Service, USDA)
 |
