Chemistry:Marschalk reaction
From HandWiki
The Marschalk reaction in chemistry is the sodium dithionite promoted reaction of a phenolic anthraquinone with an aldehyde to yield a substituted phenolic anthraquinone after the addition of acid.
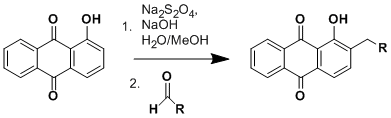
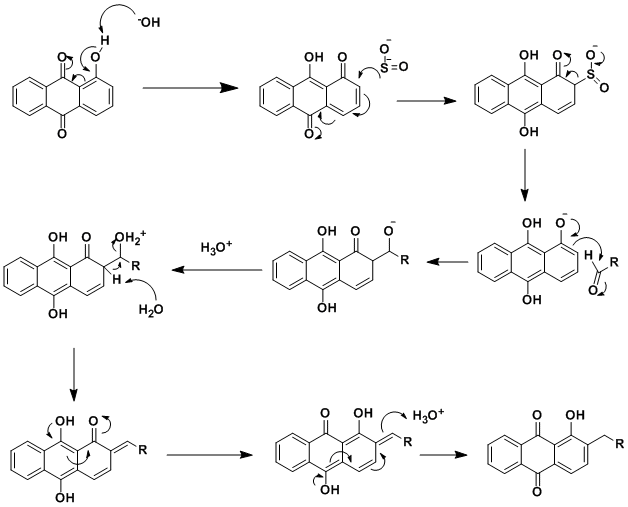
The mechanism can be found in the book Named Reactions in Organic Chemistry,[1] and its more intuitive version is provided below:
One of the first applications of this reaction was reported in 1985.[2]
References
- ↑ Mundy, Bradford P.; Ellerd, Michael G.; Favaloro, Frank G., Jr. (2005). Name Reactions and Reagents in Organic Synthesis. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 411–. ISBN 978-0-471-73986-9. https://books.google.com/books?id=ahRrPTfeqPEC&pg=PA411.
- ↑ Krohn, Karsten; Miehe, Frank (1985). "Reaction of Anthrahydroquinones with α,β-Unsaturated Carbonyl Compounds". Liebigs Annalen der Chemie 1985 (7): 1329. doi:10.1002/jlac.198519850704.
 |