Chemistry:Neopluramycin
From HandWiki
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
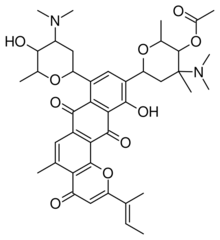
6-{2-[(2E)-2-Buten-2-yl]-8-[4-(dimethylamino)-5-hydroxy-6-methyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl]-11-hydroxy-5-methyl-4,7,12-trioxo-7,12-dihydro-4H-naphtho[2,3-h]chromen-10-yl}-4-(dimethylamino)-2,4-dimethyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-3-yl acetate
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C41H50N2O10 | |
| Molar mass | 730.855 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Neopluramycin is an antibiotic that inhibits nucleic acid synthesis. It has been isolated from the cultured broth of a strain of Streptomyces pluricolorescens as orange crystals, and analytical data and molecular weight determination are consistent with the empirical formula C41H50N2O10.[1]
Neopluramycin resembles pluramycin A, but is differentiated by its antibacterial spectrum, toxicity, thin-layer chromatography, and infrared absorption spectrum.[1]
Neopluramycin inhibits growth of Gram-positive bacteria, leukemia L-1210 in mice and Yoshida rat sarcoma cells in tissue culture.[1][2]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 "Isolation and characterization of a new antibiotic, neopluramycin". The Journal of Antibiotics 23 (7): 354–9. July 1970. doi:10.7164/antibiotics.23.354. PMID 5460277.
- ↑ "Neopluramycin, an inhibitor of nucleic acid synthesis". The Journal of Antibiotics 24 (3): 189–96. March 1971. doi:10.7164/antibiotics.24.189. PMID 4323924.
 |

