Chemistry:Nicotianamine
From HandWiki
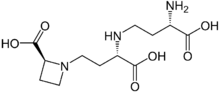
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Systematic IUPAC name
(2S)-1-[(3S)-3-{[(3S)-3-Amino-3-carboxypropyl]amino}-3-carboxypropyl]azetidine-2-carboxylic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C12H21N3O6 | |
| Molar mass | 303.31164 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Nicotianamine is a metal-chelating molecule ubiquitous in higher plants.[1] It is also used as a precursor for the synthesis of phytosiderophores which play a key role in iron uptake from the soil in graminaceous plants.[2] Biochemically, it is synthesized by the enzyme nicotianamine synthase, which uses three molecules of S-adenosylmethionine.[3]
References
- ↑ "Role of nicotianamine in the intracellular delivery of metals and plant reproductive development". The Plant Cell 15 (6): 1263–80. 2003. doi:10.1105/tpc.010256. PMID 12782722.
- ↑ Mineral Nutrition in Higher Plants, 3rd Edition. ISBN:978-0-12-384905-2
- ↑ "Nicotianamine, a novel enhancer of rice iron bioavailability to humans". PLOS ONE 5 (4): e10190. 2010. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0010190. PMID 20419136. Bibcode: 2010PLoSO...510190Z.
 |

