Chemistry:Nitrophenol
From HandWiki
Nitrophenols are compounds of the formula HOC6H5−x(NO2)x. The conjugate bases are called nitrophenolates. Nitrophenols are more acidic than phenol itself.[1]
Mono-nitrophenols
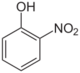 2-Nitrophenol (o-)
| |
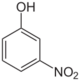 3-Nitrophenol (m-)
| |
4-Nitrophenol (p-)
| |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI |
|
| ChEMBL |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
| DrugBank |
|
| KEGG |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H5NO3 | |
| Molar mass | 139.110 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
with the formula HOC6H4NO2. Three isomeric nitrophenols exist:
- o-Nitrophenol (2-nitrophenol; OH and NO2 groups are neighboring, a yellow solid.
- m-Nitrophenol (3-nitrophenol, CAS number: 554-84-7), a yellow solid (m.p. 97 °C) and precursor to the drug mesalazine (5-aminosalicylic acid). It can be prepared by nitration of aniline followed by replacement of the amino group via its diazonium derivative.[2]
- p-Nitrophenol, yellow solid is a precursor to the rice herbicide fluorodifen, the pesticide parathion, and the human analgesic paracetamol (also known as acetaminophen).
The mononitrated phenols are often hydrogenated to the corresponding aminophenols that are also useful industrially.[1]
Di- and trinitrophenols
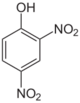
- 2,4-Dinitrophenol (m.p. 83 °C) is a moderately strong acid (pKa = 4.89).
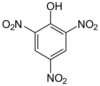
- 2,4,6-Trinitrophenol is better known as picric acid, which has a well-developed chemistry.
Safety
Nitrophenols are poisonous. Occasionally, nitrophenols contaminate the soil near former explosives or fabric factories and military plants, and current research is aimed at remediation.[3]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Gerald Booth (2007). "Nitro Compounds, Aromatic". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a17_411. ISBN 978-3527306732.
- ↑ R. H. F. Manske (1928). "m-Nitrophenol". Organic Syntheses 8: 80. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.008.0080.
- ↑ Fact sheet at atsdr.cdc.gov