Chemistry:Orange 1
From HandWiki
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
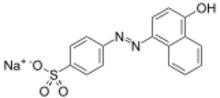
| IUPAC name
Sodium 4-[2-(4-oxonaphthalen-1-ylidene)hydrazin-1-yl]benzenesulfonate
| |
| Other names
Acid orange 20
Orange I | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 3826844 | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C16H11N2NaO4S | |
| Molar mass | 350.32 g·mol−1 |
| Hazards | |
| S-phrases (outdated) | S22, S24/25 |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Orange 1 is a red organic compound and an azo dye. It is one of the first water soluble dyes to be commercialized, and one of seven original food dyes allowed under the U.S. Pure Food and Drug Act of June 30, 1906. It is derived by the azo coupling reaction of phenyldiazonium and 2,4-diaminotoluene.
Use and discontinuation
At one time it was a popular food colorant but it was delisted in 1959 in the U.S.[1][2]
In the early 1950s, after several cases were reported of sickness in children who had eaten Halloween candy colored with the dye, the FDA conducted new, more thorough and rigorous testing on food dyes.[3] Orange 1 was outlawed for food use in 1956.[4]
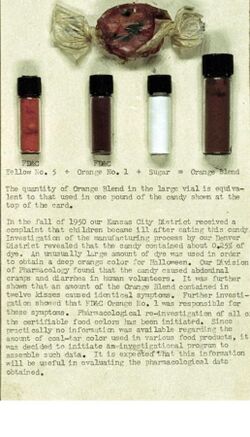
In [late] 1950[,] our Kansas City District received a complaint that children became ill after eating this candy. Investigation of the manufacturing process by our Denver District revealed that the candy contained about 0.25% of dye [FD&C Orange No. 1 and FD&C Yellow No. 5, "Orange Blend"]. An unusually large amount of dye was used in order to obtain a deep orange color for Halloween. Our Division of Pharmacology found that the candy caused abdominal cramps and diarrhea in human volunteers. It was further shown that an amount of the Orange Blend contained in twelve kisses caused identical symptoms. Pharmacological re-investigation of all the certifiable food colors has been initiated. Since practically no information was available regarding the amount of coal-tar color used in various food products, it was decided to initiate an investigational program to assemble such data. It is expected that this information will be useful in evaluating the pharmacological data obtained.
References
- ↑ Sharma, Vinita; McKone, Harold T.; Markow, Peter G. (2011). "A Global Perspective on the History, Use, and Identification of Synthetic Food Dyes". Journal of Chemical Education 88: 24-28. doi:10.1021/ed100545v.
- ↑ "News of Food; U. S. May Outlaw Dyes Used to Tint Oranges and Other Foods". The New York Times. 1954-01-19. "The use of artificial colors to make foods more attractive to the eye may be sharply curtailed by action of the United States Food and Drug Administration. Three of the most extensively used coal tar dyes are being considered for removal from the Government's list of colors certified as safe for internal and external use and consumption."
- ↑ Malia Wollan (October 5, 2016). "Brand New Hue: The Quest to Make a True Blue M&M". The New York Times Magazine. https://www.nytimes.com/interactive/2016/10/09/magazine/blue-food-coloring-mars-company.html. Retrieved October 8, 2016. "...nearly every rat and dog given Orange No. 1 showed signs of distress, ranging from weight loss to death."
- ↑ Maga, Joseph A.; Anthony T. Tu (1995). Food additive toxicology. CRC Press. p. 182. ISBN 0-8247-9245-9.