Chemistry:Oxepin
From HandWiki
|
| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Oxepine | |||
| Other names
Oxacycloheptatriene
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C6H6O | |||
| Molar mass | 94.113 g·mol−1 | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Related compounds
|
Cyclohexene oxide Oxonane | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Tracking categories (test):
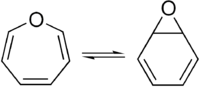
Oxepin is an oxygen-containing heterocycle consisting of a seven-membered ring with three double bonds. The parent C6H6O exists as an equilibrium mixture with benzene oxide.
The oxepin–benzene oxide equilibrium is affected by the ring substituents.[1] A related dimethyl derivative exists mainly as the oxepin isomer, an orange liquid.[2]
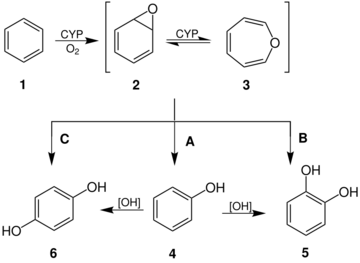
Oxepin is an intermediate in the oxidation of benzene by the cytochrome P450 (CYP).[3] Other arene oxides are metabolites of the parent arene.
References
- ↑ Vogel, E.; Günther, H. (1967). "Benzene Oxide–Oxepin Valence Tautomerism". Angewandte Chemie International Edition in English 6 (5): 385–401. doi:10.1002/anie.196703851.
- ↑ Paquette, Leo A.; Barrett, J. H. (1969). "2,7-Dimethyloxepin". Org. Synth. 49: 62. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.049.0062.
- ↑ Snyder, R.; Witz, G.; Goldstein, B. D. (1993). "The Toxicology of Benzene". Environmental Health Perspectives 100: 293–306. doi:10.1289/ehp.93100293. PMID 8354177.
 |