Chemistry:P-Dioxanone
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1,4-Dioxan-2-one | |
| Other names
para-Dioxanone
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H6O3 | |
| Molar mass | 102.089 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
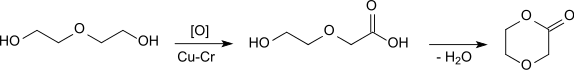
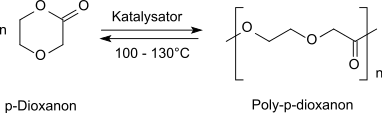
p-Dioxanone (1,4-dioxan-2-one) is the lactone of 2-(2-hydroxyethoxy)acetic acid. It is a monomer that can undergo ring-opening polymerization to give polydioxanone, a biodegradable implant material.[1] It is isomeric to trimethylene carbonate (1,3-dioxan-2-one).
Preparation
The common synthetic process for p-dioxanone is continuous gas-phase dehydrogenation of diethylene glycol on a copper or copper chromite catalyst at 280 °C.
This gives yields of up to 86%. Removal of excess diethylene glycol is crucial to the stability of the product as a monomer.[2] Further purification with recrystallization, vacuum distillation,[3] or melt crystallization[2] allows purities of >99.5% to be achieved.
Properties
Pure p-dioxanone is a white crystalline solid with a melting point of 28 °C.[4]
Uses
The oxidation of p-dioxanone with nitric acid or dinitrogen tetroxide gives diglycolic acid at 75% yield.[5]
p-Dioxanone can undergo ring-opening polymerization catalyzed by organic compounds of tin, such as tin(II) octoate[6] or dibutyltin dilaurate, or by basic alkoxides such as aluminium isopropoxide. This affords polydioxanone, a biodegradable, semicrystalline and thermally labile polymer with uses in industry and medicine.[7] Depolymerization back to the monomer is triggered at 100 °C.
References
- ↑ Sangamesh Kumbar, Cato Laurencin and Meng Deng, ed (20 February 2014). Polymeric Biomaterials in Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine. Elsevier Science. ISBN 978-0-12-396983-5.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "Recovery of dioxanone by melt crystallization" US patent 5675022, published 1995-08-23, issued 1997-10-07
- ↑ "Process for the production of 2-p-dioxanone" US patent 2142033, published 1936-07-01, issued 1938-10-27
- ↑ Lee, Sang-Won; Kim, Sung-Il; Park, So-Jin (2008). "Solubility and density of p-dioxanone in organic solvent systems". J. Korean Oil Chem. Soc. 25 (4): 429–437. https://koreascience.kr/article/JAKO200807841284700.pdf.
- ↑ , C.Y."Process for preparing diglycolic acid" US patent 3952054, issued 1976-04-20
- ↑ "Method of preparing 2-p-dioxanone polymers" US patent 3645941, issued 1972-02-09
- ↑ Bezwada, R.S.; Jamiolkowski, D.D.; Cooper, K. (1997). "Poly(p-dioxane) and its copolymers". Handbook of biodegradable polymers. A. J. Domb, Joseph Kost, David M. Wiseman. Australia: Harwood Academic Publishers. pp. 29–61. ISBN 90-5702-153-6. OCLC 38861271. https://www.worldcat.org/oclc/38861271.
 |