Chemistry:Petrenko-Kritschenko piperidone synthesis
| Petrenko-Kritschenko piperidone synthesis | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Named after | Paul Petrenko-Kritschenko | ||||||||||||||
| Reaction type | multicomponent ring-condensation | ||||||||||||||
| Reaction | |||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
| Conditions | |||||||||||||||
The Petrenko-Kritschenko reaction is a classic multicomponent-name reaction[1] that is closely related to the Robinson–Schöpf tropinone synthesis, but was published 12 years earlier.
Classic reaction
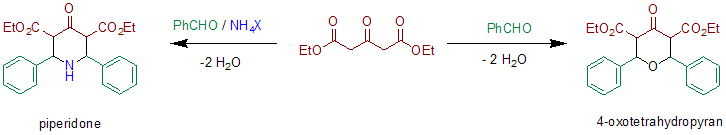
In the original publication[2] diethyl-α-ketoglurate, a derivative of acetonedicarboxylic acid, is used in combination with ammonia and benzaldehyde. The relative stereochemistry was not elucidated in the original publication, structural analysis using X-rays or NMR was not available in these days. In the absence of ammonia or ammonium salts a 4-oxotetrahydropyran is formed.[3]
In contrast to the Robinson synthesis, it does not employ dialdehydes like succinaldehyde or glutaraldehyde but simpler aldehydes like benzaldehyde. Therefore, the product of the reaction is not a bicyclic structure (see tropinone and pseudopelletierine) but a 4-piperidone. The synthesis of tropinone can be seen as a variation of the Petrenko-Kritschenko reaction in which the two aldehyde functions are covalently linked in a single molecule. Apart from the Hantzsch synthesis the Petrenko-Kritschenko reaction is one of the few examples in which a symmetric pyridine precursor can be obtained in a multicomponent ring-condensation reaction followed by an oxidation. The oxidation by chromium trioxide in acetic acid leads to a symmetrically substituted 4-pyridone, decarboxylation yields the 3,5-unsubstituted derivative.[2]
Modern variants
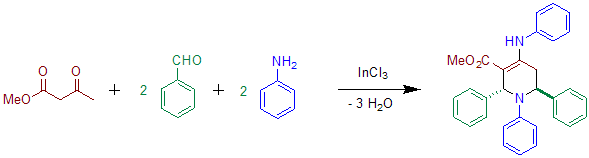
Acetoacetate can be used instead of diethyl-α-ketoglurate in the presence of indium salts.[4] The use of aniline has also been reported in the original Publication.[2] The product of this reaction shows transoid configuration of the phenyl groups at C-2 and C-6.
Natural product synthesis
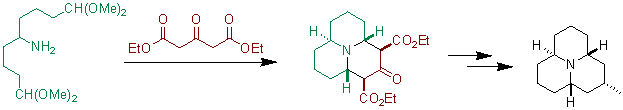
The reaction has been used to prepare precoccinellin, an alkaloid found in certain ladybugs.[1]
Applications to coordination chemistry
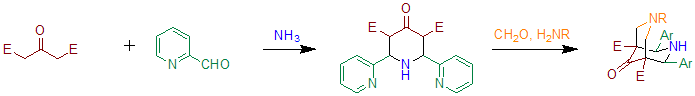
When benzaldehyde is substituted with 2-pyridinecarboxaldehyde the reaction can be used to prepare precursors for bispidone-ligands.[5] Essentially this method is based on two subsequent Petrenko-Kritschenko reactions. These ligands can be used to prepare compounds containing high-valent iron, that are able to oxidize cyclohexane in the presence of hydrogen peroxide.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Jie-Jack Li; "Name reactions in heterocyclic chemistry"; 2005 John Wiley & Sons; ISBN:0-471-30215-5; pp313
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 P. Petrenko-Kritschenko "Über die Kondensation des Acetondicarbonsäureesters mit Aldehyden, Ammoniak und Aminen" Journal für Praktische Chemie Volume 85, Issue 1, pages 1–37, 20 May 1912; doi:10.1002/prac.19110850101
- ↑ P. Petrenko-Kritschenko "Über Tetrahydropyronverbindungen" Journal für Praktische Chemie; Volume 60, Issue 1, pages 140–158, 27 December 1899; doi:10.1002/prac.18990600114
- ↑ Clarke, Paul A.; Zaytzev, Andrey V.; Whitwood, Adrian C. "Pot, atom and step economic (PASE) synthesis of highly functionalized piperidines: a five-component condensation" Tetrahedron Letters Volume 48, Issue 30, 23 July 2007, Pages 5209–5212; doi:10.1016/j.tetlet.2007.05.141
- ↑ Comba, Peter; Kerscher, Marion; Merz, Michael; Müller, Vera; Pritzkow, Hans; Remenyi, Rainer; Schiek, Wolfgang; Xiong, Yun "Structural Variation in Transition-Metal Bispidine Compounds" Chemistry – A European Journal Volume 8, Issue 24, pages 5750–5760, 16 December 2002; doi:10.1002/1521-3765(20021216)8:24<5750::AID-CHEM5750>3.0.CO;2-P
External links
- A picture of Paul Petrenko-Kritschenko taken at the Kazan School of Chemistry in 1928 (1st row, first on the left): http://www.ksu.ru/chmku/images/30b.jpg
 |