Chemistry:Phenylahistin
From HandWiki
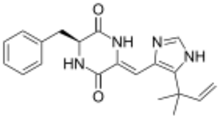
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(3S,6Z)-3-Benzyl-6-{[5-(2-methyl-3-buten-2-yl)-1H-imidazol-4-yl]methylene}-2,5-piperazinedione
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C20H22N4O2 | |
| Molar mass | 350.422 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Phenylahistin is a metabolite produced by the fungus Aspergillus ustus[1] that belongs to a class of naturally occurring 2,5-diketopiperazines featuring a dehydrohistidine residue that exhibit important biological activities, such as anti-cancer or neurotoxic effects.[2]
Phenylahistin is a microtubule binding agent that exhibits cytotoxic activities against a wide variety of tumor cell lines.[3] A series of synthetic analogs were prepared to remove the chirality and optimize biological activity. These studies led to the potent anti-tumor agent plinabulin, which is active in multidrug-resistant (MDR) tumor cell lines.[4]
References
- ↑ "(−)-Phenylahistin: A new mammalian cell cycle inhibitor produced by aspergillus ustus". Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters 7 (22): 2847–2852. 1997. doi:10.1016/S0960-894X(97)10104-4.
- ↑ Borthwick AD (2012). "2,5-Diketopiperazines: Synthesis, Reactions, Medicinal Chemistry, and Bioactive Natural Products". Chemical Reviews 112 (7): 3641–3716. doi:10.1021/cr200398y. PMID 22575049.
- ↑ "Antitumor activity of phenylahistin in vitro and in vivo.". Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry 63 (6): 1130–1133. 1999. doi:10.1271/bbb.63.1130. PMID 10427703.
- ↑ "NPI-2358 is a tubulin-depolymerizing agent: in-vitro evidence for activity as a tumor vascular-disrupting agent". Anticancer Drugs 17 (1): 25–31. 2006. doi:10.1097/01.cad.0000182745.01612.8a. PMID 16317287.
 |

