Chemistry:QS21
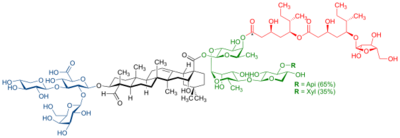
QS-21 is a purified plant extract that enhances the ability of the immune system to respond to vaccine antigens. It is derived from the soap bark tree (Quillaja saponaria), which is native to the country of Chile . Isolation of QS-21 destroys the soap bark tree, which has resulted in regulation of the tree by the governments where it is grown.[1]
The extract contains water soluble triterpene glucoside compounds, which are members of a family of plant-based compounds called saponins.
It is currently being tested as an immunologic adjuvant in various vaccines in attempts to improve their efficacy. It is believed to enhance both humoral and cell-mediated immunity. Success has been limited in synthetically producing QS-21 with similar adjuvant activity to the isolated natural product.[2]
QS-21 is currently under clinical evaluation as an additive for various trial vaccines, including those for HIV, malaria and cancer. As of 2002[update], it had been tested in more than 3000 patients in 60 clinical trials. It has a component of the FDA-approved Shingrix shingles vaccine.[3]
See also
References
- ↑ Ragupathi G, Gardner JR, Livingston PO, Gin DY. "Natural and synthetic saponin adjuvant QS-21 for vaccines against cancer". Expert Rev Vaccines 10: 463–70. doi:10.1586/erv.11.18. PMID 21506644.
- ↑ Chea EK, Fernández-Tejada A, Damani P, Adams MM, Gardner JR, Livingston PO, Ragupathi G, Gin DY. "Synthesis and preclinical evaluation of QS-21 variants leading to simplified vaccine adjuvants and mechanistic probes". J Am Chem Soc 134: 13448–57. doi:10.1021/ja305121q. PMID 22866694.
- ↑ "BLA Approval". Food and Drug Administration. October 20, 2017. https://www.fda.gov/downloads/BiologicsBloodVaccines/Vaccines/ApprovedProducts/UCM581750.pdf.
External links
