Chemistry:Quinfamide
From HandWiki
Short description: Chemical compound with anti-parasitic properties
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
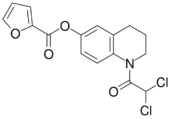
| Formula | C16H13Cl2NO4 |
| Molar mass | 354.18 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Quinfamide is a drug that has anti-parasitic properties.[1]
Synthesis
Quinfamide is one of a relatively small family of antiamoebic compounds containing a dichloroacetamide function.[citation needed]

The synthesis begins by amidation of 6-hydroxytetrahydroquinoline with dichloroacetyl chloride. The sequence is completed by acylation with 2-furoyl chloride.
References
- ↑ "Nitazoxanide compared with quinfamide and mebendazole in the treatment of helminthic infections and intestinal protozoa in children". The American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 66 (3): 251–4. March 2002. doi:10.4269/ajtmh.2002.66.251. PMID 12139216.
- ↑ Bailey, Denis Mahlon, "1-(Halogenated-acetyl)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-6-quinolinols and esters thereof", US patent 3997542, published 1976-12-14, assigned to Sterling Drug Inc.
- ↑ "1-(Dichloroacetyl)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-6-quinolinol esters. New potent antiamebic agents". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 22 (5): 599–601. May 1979. doi:10.1021/jm00191a031. PMID 458814.
 |
