Chemistry:Rugulovasine
From HandWiki
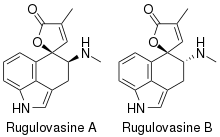
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
IUPAC name
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C16H16N2O2 | |
| Molar mass | 268.316 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Rugulovasines are bio-active alkaloids made by Penicillium.[1] Rugulovasine A and B bind strongly to the 5-HT1A, 5-HT2A, and 5-HT2C receptors, but lack meaningful binding affinity towards the α1 adrenergic and dopamine receptors.[2] Little is known about the in vivo activity of Rugulovasine A and B, although they have hypotensive effects in cats.[3]
References
- ↑ Dorner, JW; Cole, RJ; Hill, R; Wicklow, D; Cox, RH (September 1980). "Penicillium rubrum and Penicillium biforme, new sources of rugulovasines A and B.". Applied and Environmental Microbiology 40 (3): 685–7. doi:10.1128/aem.40.3.685-687.1980. PMID 7425621.
- ↑ Bartoccini, Francesca; Regni, Alessio; Retini, Michele; Piersanti, Giovanni (6 May 2022). "Asymmetric Total Synthesis of All Rugulovasine Stereoisomers and Preliminary Evaluation of Their Biological Properties" (in en). European Journal of Organic Chemistry 2022 (17). doi:10.1002/ejoc.202200315. ISSN 1434-193X.
- ↑ Nagaoka, A; Kikuchi, K (January 1972). "Pharmacological studies of new indole alkaloids, rugulovasine A and B hydrochloride. II. Hypotensive mechanism of both alkaloids in the anesthetized cats.". Arzneimittel-Forschung 22 (1): 143–6. PMID 5066989.
 |

